Volume 24, Number 12—December 2018
Research
Rat Hepatitis E Virus as Cause of Persistent Hepatitis after Liver Transplant
Figure 5
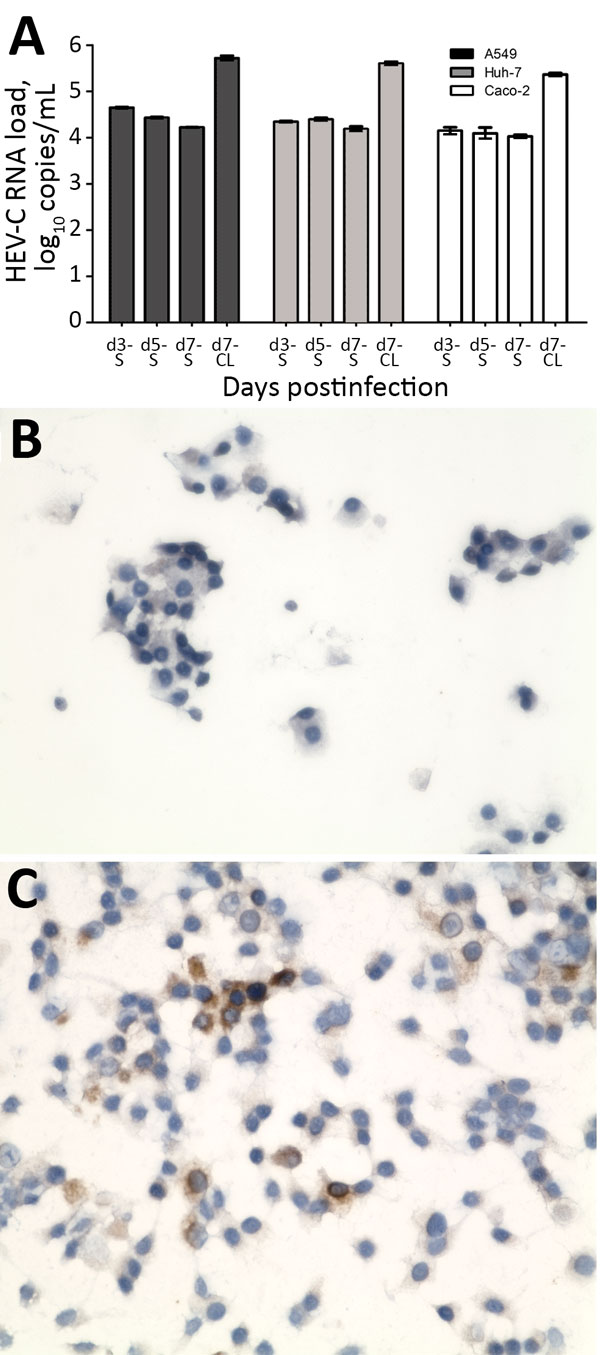
Figure 5. Isolation of HEV-C from 56-year-old male patient’s feces in cell culture, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong. A) HEV-C RNA loads in culture S and day-7 CL of A549, Huh-7, and Caco-2 cell lines after inoculation by patient’s filtered fecal suspension. Mean of 3 replicates; error bars indicate SEM. B) Uninfected A549 cell monolayer stained with anti–HEV-C polyclonal antiserum. C) Infected A549 cell monolayer stained with anti–HEV-C polyclonal antiserum. Original magnification ×400. CL, cell lysate; HEV, hepatitis E virus; S, supernatant.
Page created: November 20, 2018
Page updated: November 20, 2018
Page reviewed: November 20, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.