Volume 25, Number 4—April 2019
Research
Differences in Neuropathogenesis of Encephalitic California Serogroup Viruses
Figure 4
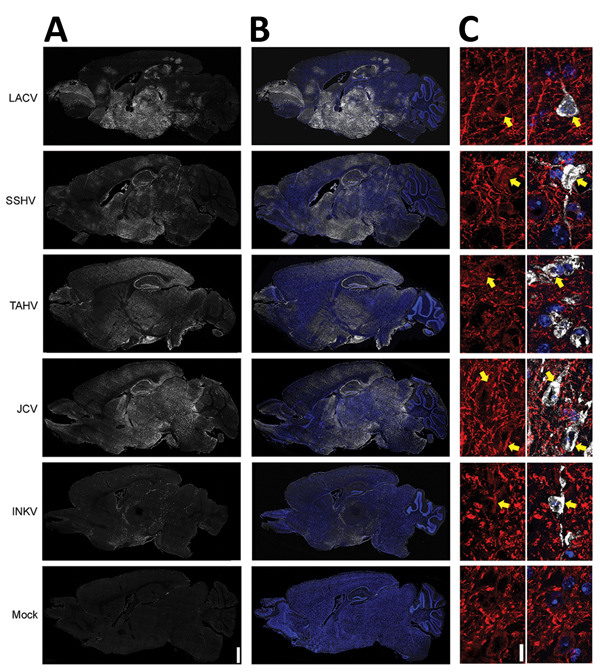
Figure 4. Viral antigen in brains of adult and aged mice exhibiting neurologic disease after intranasal inoculation of 104 PFU of California serogroup (CSG) viruses in study of neuropathogenesis. We evaluated >4 brains from mice infected with each CSG virus, except INKV (where only 3 brains from mice with neurologic disease were available), for viral immunoreactivity. A, B) Representative images showing distribution of virus (white) and virus merged with Hoechst nuclear stain (blue) via full-section brain scans. Scale bar indicates 1 mm. C) Maximum intensity projections of 5-μm confocal z-stacks (original magnification ×63) of brains of mice infected with the indicated CSG virus, labeled for virus (white) and the neuronal marker microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2; red). Left panels demonstrate MAP2 staining alone, and right panels are overlays of virus, MAP2, and Hoechst nuclear stain (blue). Yellow arrows indicate the soma of neurons where both viral and MAP2 immunoreactivity are found. Scale bar indicates 10 μm. INKV, Inkoo virus; JCV, Jamestown Canyon virus; LACV, La Crosse virus; SSHV, snowshoe hare virus; TAHV, Tahyna virus.