Novel Subclone of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Sequence Type 11 with Enhanced Virulence and Transmissibility, China
Kai Zhou
1, Tingting Xiao
1, Sophia David
1, Qin Wang, Yanzi Zhou, Lihua Guo, David Aanensen, Kathryn E. Holt, Nicholas R. Thomson, Hajo Grundmann
2, Ping Shen
2, and Yonghong Xiao
2
Author affiliations: First Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology (Shenzhen People’s Hospital); Shenzhen, China (K. Zhou); The Second Clinical Medical College of Jinan University, Shenzhen (K. Zhou); Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China (T. Xiao, Q. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Guo, P. Shen, Y. Xiao); Centre for Genomic Pathogen Surveillance, Cambridge, UK (S. David, D. Aanensen); University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia (K.E. Holt); London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, London, UK (K.E. Holt, N.R. Thomson); Wellcome Trust Sanger Centre, Cambridge (N.R. Thomson); University of Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany (H. Grundmann)
Main Article
Figure 1
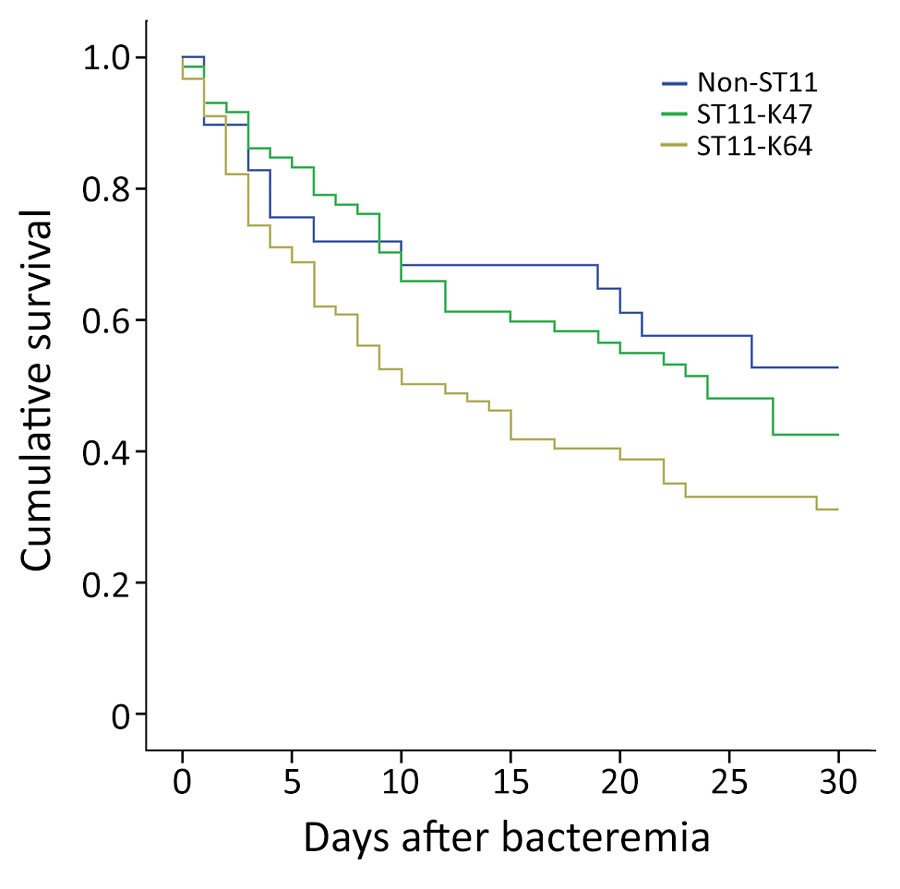
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meier survival estimates for patients with bloodstream infections caused by ST11-KL47, ST11-KL64, and non-ST11 CRKP, China, 2013–2017. A significant difference was found in the 30-day mortality among the 3 groups (p = 0.039). ST11-KL64–infected patients showed significantly higher overall 30-day mortality than ST11-KL47–infected patients (62.2% vs. 52.8%; p = 0.039) and non-ST11 CRKP–infected patients (62.2% vs. 44.8%; p = 0.05). No significant difference in 30-day mortality was found between patients infected with ST11-KL47 and non-ST11 CRKP (52.8% vs. 44.8%, p = 0.529). CRKP, carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae; KL, capsular loci; ST, sequence type.
Main Article
Page created: January 17, 2020
Page updated: January 17, 2020
Page reviewed: January 17, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
