Volume 26, Number 8—August 2020
Research
Factors Associated with Prescription of Antimicrobial Drugs for Dogs and Cats, United Kingdom, 2014–2016
Figure 1
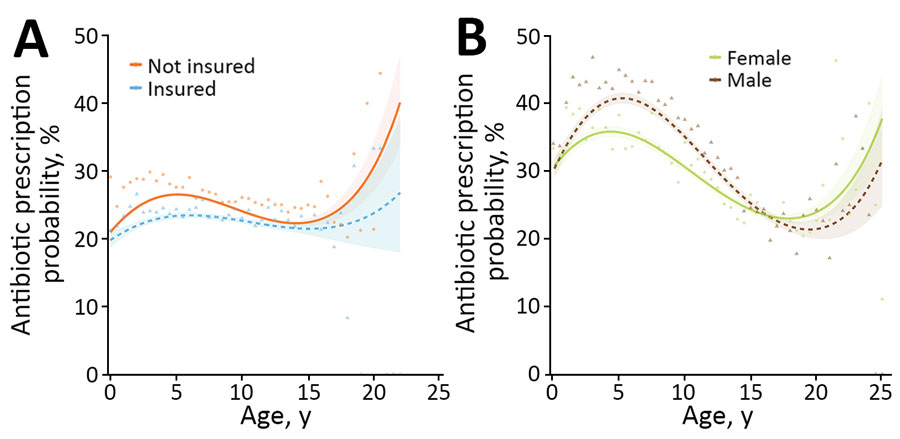
Figure 1. Results from 2 multivariable mixed effect logistic regression models predicting probability of systemic antimicrobial prescription in study of factors associated with prescription of antimicrobial drugs for dogs and cats, United Kingdom, 2014–2016. Modeling is shown for sick dogs (A) and cats (B) against age of the animal at time of consultation, in years. For dogs, an interaction term considering current insurance status has been included; for cats, an interaction term considering sex has been included. Lines refer to predicted probability; shading relates to 95% CIs for such predictions. Points and triangles are plotted to show original data points expressing the percentage of animals of each relevant age group (rounded to 0.5-year groups) for which a systemic antimicrobial was prescribed, according to the dataset analyzed.