Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Research
Comparative Omics Analysis of Historic and Recent Isolates of Bordetella pertussis and Effects of Genome Rearrangements on Evolution
Figure 5
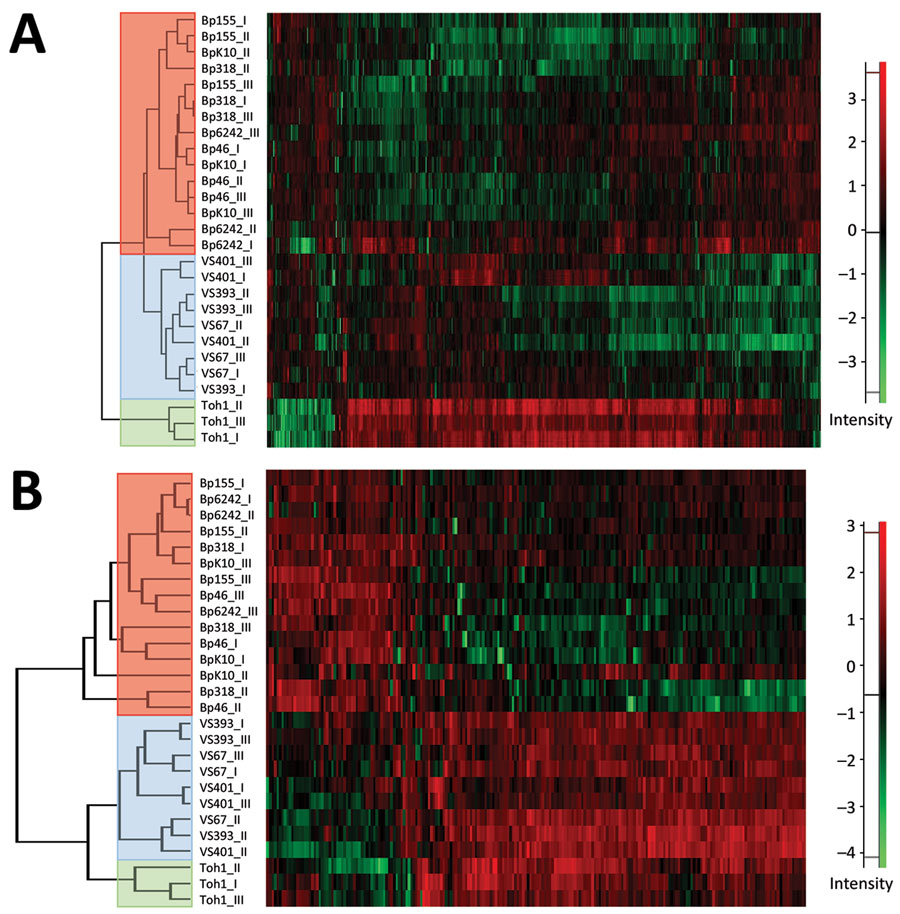
Figure 5. Heatmaps showing hierarchical clustering performed on Z-score normalized log2-transformed label-free intensity values of cell-associated (A) or secreted (B) protein fractions of historic and recent isolates of Bordetella pertussis from the Czech Republic and the Tohama I strain. Clustering of recent, historic, and Tohama I strains is indicated by red, blue, and green, respectively. Scale bars indicate intensity of proteins normalized by Z-score.
Page created: September 01, 2020
Page updated: December 21, 2020
Page reviewed: December 21, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.