Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Research
Comparative Omics Analysis of Historic and Recent Isolates of Bordetella pertussis and Effects of Genome Rearrangements on Evolution
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
Abstract
Despite high vaccination coverage, pertussis is increasing in many industrialized countries, including the Czech Republic. To better understand Bordetella pertussis resurgence, we analyzed historic strains and recent clinical isolates by using a comparative omics approach. Whole-genome sequencing showed that historic and recent isolates of B. pertussis have substantial variation in genome organization and form separate phylogenetic clusters. Subsequent RNA sequence analysis and liquid chromatography with mass tandem spectrometry analyses showed that these variations translated into discretely separated transcriptomic and proteomic profiles. When compared with historic strains, recent isolates showed increased expression of flagellar genes and genes involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and decreased expression of polysaccharide capsule genes. Compared with reference strain Tohama I, all strains had increased expression and production of the type III secretion system apparatus. We detected the potential link between observed effects and insertion sequence element–induced changes in gene context only for a few genes.
Bordetella pertussis is a gram-negative, strictly human pathogen of the respiratory tract and the major causative agent of whooping cough. This highly contagious disease is especially severe in infants and remains a major cause of infant illness and death worldwide, predominantly in industrialized countries (1). Although pertussis is a vaccine-preventable disease, increased incidence is being observed in some countries that have highly vaccinated populations, including the Czech Republic (2–4). Although several factors are contributing to pertussis resurgence in these countries (5–7), the 2 prominent factors are incomplete and short-lived immunity induced by current acellular vaccines (8–10) and genetic variation, leading to escape from immunity by antigenic variation (11–13).
B. pertussis has an efficient mechanism of genome structure diversification because it contains >200 copies of insertion sequence 481 (IS481) in its genome (14). IS element–mediated homologous recombination results in excision or insertion of flanking genome regions and leads to genome reduction and decay (14–16), as well as genome rearrangements (17,18) and large duplications (19). Furthermore, a previous study indicated that gene order rearrangements associated with IS elements can alter gene expression profiles in B. pertussis (20). Recently, we have shown that, besides their effect on genome structure and stability, ISs can affect expression profiles of neighboring genes by IS element–specific promoters (21).
On the basis of these observations, we hypothesized that strains with different genomic organization should display altered global transcriptomic and, consequently, proteomic profiles, and thereby genome rearrangements might contribute to strain variation and adaptation. To validate this assumption, we have performed genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic analyses of recent clinical isolates from the Czech Republic obtained during 2008–2015, previously characterized vaccine strains isolated during 1954–1965 (22) (hereafter referred to as historic strains), and the reference strain Tohama I.
Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
Recent isolates of B. pertussis from the Czech Republic were obtained from the National Institute of Public Health in Prague (Table 1). Historic strains from the Czech Republic (22) and reference strain Tohama I (23) have been described. All strains were cultivated on Bordet-Gengou agar plates supplemented with 15% sheep blood for 3–4 days at 37°C. For liquid cultures, bacteria were grown in Stainer-Scholte medium (24) supplemented with 0.1% cyclodextrin and 0.5% casamino acids (Difco, https://www.fishersci.com) at 37°C. To harvest samples for DNA, RNA, and protein isolation, B. pertussis cells were grown overnight in Stainer-Scholte medium to mid-exponential phase of growth (optical density ≈1.0). Three independent cultivations were performed to collect 3 biologic replicates of each of the strains for RNA and protein isolation.
Genomic Analyses
For the genome organization analysis, genomic sequences were aligned by using the progressive Mauve algorithm (25) and clustered on the basis of their genome organization similarity by using the maximum-likelihood for the gene order pipeline (26). For single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) analysis, IS elements within the genomes were masked with Ns, and resulting sequences were aligned by using Mugsy software (27). SNPs were extracted by using custom scripts (https://genohub.com). Maximum-parsimony phylogenetic analysis was performed on sequences with masked IS elements by using the kSNP3 program with a k number of 23 (28). The unrooted phylogenetic tree was visualized by using iTOL (29).
RNA Isolation, Sequencing, and Data Analysis
We provide information on RNA isolation, sequencing, and data analysis (Appendix 1). RNA sequencing data from sequencing runs were deposited in the European Nucleotide Archive under project accession no. PRJEB34096. We defined significance as a q value <0.05 (p value adjusted for multiple testing correction [Appendix 1]).
Protein Sample Preparation and Proteomic Analysis
We compiled information on protein sample preparation and label-free proteomic analysis, which used liquid chromatography with mass tandem spectrometry analyses (Appendix 1). Proteomics data were deposited in the ProteomeXchange Consortium by using the PRIDE partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD015184.
Genome Organization and Content of Recent Isolates
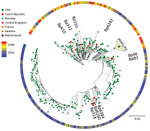
We determined complete de novo genome assemblies of 9 recent isolates of B. pertussis strains collected in the Czech Republic during 2008–2015 from patients representing different age groups and vaccination status (Table 1). Genotyping of recent strains showed that they belonged to ptxP3 lineage. SNP-based phylogenetic analysis of these strains and >350 complete B. pertussis genome sequences currently deposited in GenBank (Appendix 2 Table 1) showed that recent B. pertussis isolates cluster with ptxP3 isolates from other countries, demonstrating worldwide spread and lack of geographic signature (Figure 1). The genome alignment of recent isolates and previously characterized historic strains belonging to the ptxP1 lineage (22) showed that all genomes contain large-scale structural rearrangements (Figure 2, panel A). According to their genome organization, sequenced strains could be classified into 8 groups. None of the historic strains clustered with any of the recent isolates. The separation of these 2 groups was verified by using a maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree, which was constructed on the basis of the genome organization of all sequenced strains from the Czech Republic (Figure 2, panel B).
To check whether there are also sequence signatures differentiating these 2 groups of strains, we performed SNP analysis, which yielded 35 SNPs (15 synonymous, 13 nonsynonymous, and 7 intergenic) (Appendix 2 Table 2) and distinguished historic and recent isolates. Variants found in historic strains were also present in Tohama I. One of the new SNPs specific for recent isolates was identified in the promoter region of the bteA gene, which encodes the type III secretion system (T3SS) effector. Approximately one third of the SNPs have been reported to be specific for the ptxP3 lineage isolates from other countries (30). When compared with those of historic strains, the genome size of recent isolates was substantially reduced, thereby confirming ongoing gene loss within the global population of B. pertussis (Appendix 2 Table 3). Analysis of genome alignments showed 2 regions of difference (RD) between the 2 groups of strains from the Czech Republic, which corresponded to previously identified regions RD3 and RD10 (20). Although RD3 (28.7 kb, spans genes BP0910A–BP0937) is absent in all recent isolates, the RD10 (25.1 kb, spans genes BP1948–BP1968) is absent in all recent isolates and historic strain V67.
Transcriptomic Profiles and Genomic Structure Alterations
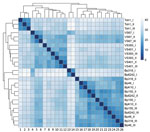
Total RNA was isolated from biologic triplicates of B. pertussis Tohama I strain; historic strains VS393, VS67, and VS401; and recent isolates Bp318, Bp155, Bp46, Bp6242, and BpK10 and analyzed by using RNA sequencing. These strains were selected on the basis of genome organization and phylogenetic distances to encompass the highest variability among the studied strains (Figure 2, panel B). Hierarchical clustering of RNA sequence data showed that samples from both groups of strains from the Czech Republic clustered separately from each other and from Tohama I (Figure 3). Consistent with phylogenetic analysis (Figure 2, panel B), we found that samples of strain VS67 formed a separate cluster. These analyses suggested that among historic strains, the VS67 strain displays closest distance to recent strains, which is consistent with our previous observation that the VS67 strain clusters together with a recent U.S. isolate (22).
Differential expression (DE) analysis identified 78, 124, and 115 significantly (q<0.05 for all comparisons) modulated B. pertussis genes (–1>log2 FC>1) between recent isolates and historic strains, recent isolates and Tohama I, and historic strains and Tohama I, respectively (Appendix 2 Table 4). Among the DE genes, 30 were up-regulated in recent isolates compared with historic strains, including those encoding the flagella apparatus (flgB-J), LuxR (BP1969), and ArsR (BP2946) families of transcriptional regulators, phosphoglucomutase (pgm), phosphoglucose isomerase (pgi), and nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase (nadC). Conversely, among the 48 DE genes down-regulated in recent isolates were genes encoding the polysaccharide capsule proteins (kpsEMT), several ABC transporters, and central metabolism enzymes, including those involved in tryptophan synthesis (trpDEG). Expression of several virulence factors, including pertactin, tracheal colonization factor, filamentous hemagglutinin, and pertussis toxin subunit S3, was significantly up-regulated in recent isolates. However, the increase did not reach the 2-fold threshold. A recent isolate-specific SNP, which was identified in the promoter region of the bteA gene, did not result in a significant change of gene expression (Appendix 2 Table 4). Among the DE genes that showed increased expression in both groups of strains from the Czech Republic compared with Tohama I, we identified numerous genes within the T3SS bcs/btr locus, including bsp22, bopN, bopB, and bopD and several genes involved in sulfate metabolism (cysADITW).
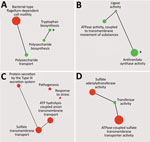
Gene ontology enrichment (Figure 4, panel A) showed that within the set of genes, which were significantly modulated between recent and historic isolates, categories such as bacterial type flagellum-dependent cell motility, polysaccharide biosynthesis, and tryptophan biosynthesis were highly enriched. Conversely, when we compared both groups of isolates from the Czech Republic to Tohama I (Figure 4, panel C), genes associated with sulfate transmembrane transport, pathogenesis, and protein secretion by the type III secretion system terms were enriched among the DE genes.
Clustering of Proteomic Profiles of Recent Isolates, Historic Strains, and Tohama I Strain
The cell-associated (bacterial pellets) and cell-free (culture supernatants) fractions of selected B. pertussis strain cultures were analyzed by using liquid chromatography with mass tandem mass spectrometry. First, hierarchical clustering of the cell-associated protein profiles showed that consistent with RNA sequencing data, strains from the Czech Republic cluster separately from Tohama I and despite high variability among biologic replicates, separation of historic and recent strains was still apparent (Figure 5, panel A). Similarly, hierarchical clustering of secreted proteins indicated that recent isolates cluster apart from historic strains and Tohama I (Figure 5, panel B).
Label-free quantification of cell-associated protein intensities identified 33, 132, and 87 proteins showing significantly changed abundance between recent and historic strains, recent strains and Tohama I, and historic strains and Tohama I, respectively (Appendix 2 Table 5). In good correlation with transcriptomic data, we found that protein levels of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA lyase (BP3695), ArsR family transcriptional factor BP2946, small lipoprotein BP2782, and nicotinate-nucleotide diphosphorylase NadC were increased, but levels of several central metabolism enzymes (BP0624–BP0629), tryptophan synthesis genes, and polysaccharide capsule proteins were decreased in recent isolates compared with historic strains (Table 2). Also in support of RNA sequencing data, we determined that various components of the T3SS apparatus and several proteins involved in metabolism of sulfate showed increased abundance compared with Tohama I (Table 3). All strains from the Czech Republic produced pertactin, but flagellar proteins were not detected in any of the studied strains.
Label-free quantification analysis of secreted proteins showed that 121, 130, and 43 proteins displayed significant changes in abundance between recent and historic strains, recent strains and Tohama I, and historic strains and Tohama I, respectively (Appendix 2 Table 6). Levels of several secreted proteins were in good agreement with transcriptomic data (e.g., strains from the Czech Republic and in particular recent isolates secreted increased amounts of several T3SS proteins compared with Tohama I) (Table 3). Abundance of all pertussis toxin subunits and associated transport protein PtlE was higher in recent isolates than in historic strains, which suggests that some of the differences between the ptxP1 and ptxp3 strains are also manifested at the level of protein secretion.
Changes in Genome Structure and Alterations in Gene Expression
Considering the observed differences between historic and recent strains, we attempted to track back the modulated gene expression profiles to alterations in the genome sequence and structure. Because our SNP analysis (Table 2) suggested that there were no SNPs that could explain the altered expression of the DE genes, we have additionally inspected the upstream regions of all DE genes for larger sequence variations. We identified such variations in 4 genes. The gene toh_02779 (BP2827) was preceded by an IS481 element in Bp155, Bp6242, and BpK10, but not in other strains. In addition, 3 DE genes with an upstream IS481 element had varying gene context further upstream of the transposase in the studied strains (Table 4). Apparently, the observed differences in expression of these genes could be potentially linked to the upstream IS elements.
We then tested the possible effect of genome rearrangements on the distance of the DE genes from the origin of replication (oriC), a parameter that can greatly affect gene expression (31). We determined the distance from oriC to all the genes significantly deregulated between recent and historic strains, and although expression of some of the genes inversely correlated with the distance from oriC, the differences were not significant.
We conducted a comparative study analyzing the link between genomic organization, gene expression profiles, and protein production/secretion in historic and recent strains of B. pertussis. Our results indicate that global changes in genomic structures observed between historic and recent isolates of B. pertussis from the Czech Republic translated into different gene expression and protein production profiles. Similarly to other countries, the IS element–driven recombination led to large changes in genomic structures and to considerable gene loss in the isolates from the Czech Republic over the past 50–60 years. Results of our integrated omics analysis support our assumption that genomic rearrangements might affect global expression profiles and phenotypic diversity in B. pertussis. Hierarchical clustering of our omics data indicates that strains, which cluster apart at genomic structure level, also have distinct transcriptomic and proteomic profiles.
Given the extent of genome structural variability among both groups of strains, the number of differentially expressed genes was rather low (≈2% of all coding genes). Earlier DNA microarray studies suggested that gene expression profiles between ptxP1 strains and recent resurgence-associated ptxP3 lineage differ only subtly (32,33). Although we have identified an increased number of significantly modulated genes, our data on historic (ptxP1) and recent (ptxP3) isolates are consistent with these reports. None of the gene expression alterations could be shown to result from nucleotide polymorphism, and only a few could be linked to IS element–induced changes in the local gene context. Upstream of the IS481 element adjacent to the BP1492 gene, we identified the BPt20 tRNA gene in most historic strains and Tohama I, which is, however, missing in recent isolates and historic strain VS67. Thus, it is possible that the activity of the strong tRNA promoter is responsible for increased expression of the BP1492 gene in historic strains. Also, the presence of an IS481 element in front of the BP2827 gene in Bp155, Bp6242, and BpK10 strains might explain the increased expression of this gene in recent isolates. In support of this possibility, when compared with all other strains lacking this IS element, these 3 recent isolates showed highly increased expression of this gene. It is also possible that the observed differences in gene expression between historic and recent strains result from changes in genome organization or gene loss. Bacterial chromosome organization appears to favor a conserved gene order (34), and changes in genome architecture and topology can affect gene expression (35,36). Therefore, it is conceivable that genome rearrangements, resulting in changes in gene order and orientation or in large deletions, might affect transcriptomic profiles in B. pertussis.
We have identified 2 previously characterized regions of difference between historic and recent strains, which might offer alternative explanation for the observed differences in gene expression (20,37). Consistent with these reports, our reports found that genes within RD3 and RD10 are missing in all recent isolates. RD3 contains 2 putative transcriptional regulators (BP0924 and BP0928) of unknown function. Thus, it is probable that absence of these regulators in recent isolates might be accountable for some of the identified alterations in gene expression.
Furthermore, RNA sequencing analysis identified 2 transcriptional regulator genes that are expressed at higher levels in recent isolates, and suggested that some of the observed differences between historic and recent strains might also result from altered expression of regulatory genes. BP1969, which encodes a LuxR family transcriptional factor, lies upstream of the BP1970 and BP1971 genes, which encode phosphoglucomutase Pgm and phosphoglucose isomerase Pgi. Similarly to BP1969, pgm and pgi genes were significantly up-regulated in recent strains. Therefore, we assume that the BP1969 gene probably represents a cognate regulator for these glycolytic genes. Besides its role in glycolysis, Pgm catalyzes the generation of sugar nucleotides needed for biosynthesis of lipopolysaccharide and cell wall and was shown to be required for virulence of B. bronchiseptica (38) and several other pathogens (39,40). Strains lacking the pgm gene showed increased susceptibility to antimicrobial peptides and were attenuated in in vivo models of infection (38–40). Pgi catalyzes the second step in glycolysis and was shown to be required for virulence of Xanthomonas campestris (41). Thus, we presume that increased expression and production of both enzymes might contribute to increased virulence and fitness of the ptxP3 lineage.
Among other modulated genes, expression of numerous genes within the operon encoding the flagellar apparatus was significantly increased in recent isolates. However, we could not corroborate this finding because we did not detect any flagellar proteins in our samples. Recent observations suggest that B. pertussis is motile under modulatory Bvg-conditions (42) and that motility genes are up-regulated during adaptation to the mouse respiratory tract (43). Apparently, in vivo conditions, prevailing during B. pertussis infections in mice, cannot be completely reproduced under standard laboratory growth conditions, as documented (43,44), and further experiments are required to determine whether the increased expression translates into higher motility of recent isolates and contributes to improved ability of ptxP3 strains to colonize the respiratory tract (33).
Conversely, expression of an almost complete operon that encodes genes involved in polysaccharide capsule synthesis was substantially down-regulated in recent isolates. This observation is consistent with that of a previous report (45) and demonstrates that capsule proteins are produced by B. pertussis. This finding also involves the protein responsible for polysaccharide biosynthesis TviD (BP1618), which has been reported to be encoded by a pseudogene (14).
Data on the role of the capsule in the virulence and physiologic fitness of B. pertussis are contradictory. Hoo et al. (46) showed that the capsule proteins are expressed during the infection and are required for an efficient colonization of mouse lungs. In contrast, in vitro assays showed that the capsule did not protect B. pertussis cells from phagocytosis and serum killing (45) and that the capsule locus was not expressed during infection of mouse respiratory tract (43). Therefore, it is difficult to assess whether reduced production of capsule proteins provides recent strains with any selective advantage. Nevertheless, the capsular polysaccharides of several gram-negative bacteria are highly immunogenic and were used to formulate carbohydrate–protein conjugate vaccines (47). Therefore, it is possible that in circulating isolates of B. pertussis, reduced production of the capsule synthesis apparatus contributes to evasion from the host immune response.
Our omics data manifest that, in spite of being isolated at the similar period of time, historic strains are substantially distinct from the reference strain Tohama I. Previous genomic analyses documented that several different clusters of B. pertussis circulated in Europe and the United States already in prevaccine and early vaccine eras and that their genomes were different from Tohama I (20,37). Our results with strains from the Czech Republic are consistent with these observations and also confirm this distinction at the transcriptomic and proteomic levels. For example, expression and production of various sulfate metabolism factors (sbp, cysT, cysA) were strongly reduced in Tohama I compared with strains from the Czech Republic. Likewise, we demonstrated that recent and historic strains had significantly increased expression, production, and secretion of several T3SS components. This observation is consistent with previous reports (48,49) and confirms that not only recent isolates but also low-passage historic strains of B. pertussis are T3SS proficient (48,49). We conclude that, in agreement with previous reports (37,50), the Tohama I strain is not a good representative of the circulating B. pertussis population.
Collectively, our data suggest that, besides shaping the evolution of B. pertussis on a genomic scale, the genome rearrangement and genome reduction processes also affect global transcriptomic and proteomic profiles. In agreement with results of a previous report (20), we assume that these mechanisms counterbalance the low level of genetic variability observed in this pathogen and strongly contribute to adaptation of the global population of B. pertussis.
Dr. Dienstbier is a postdoctoral fellow in the Laboratory of Post-transcriptional Control of Gene Expression, Institute of Microbiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Prague, Czech Republic. Her research interests are genomics and transcriptomics of B. pertussis strains and molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of pertussis.
Acknowledgments
We thank Richard Neuboeck helping to setup software for some of the analyses, Michael Weigand for providing the sequence of the oriC region, and Karel Harant and Pavel Talacko for performing the liquid chromatography with mass tandem spectrometry analyses runs.
This study was supported by Czech Health Research Council (http://www.azvcr.cz) grant 16-30782A to B.V., Czech Research Foundation (http://www.qacr.cz) grant 19-12338S to B.V., institutional funding RVO61388971, and a mobility grant from the Czech Academy of Sciences (MSM200201702) to A.D. This study was also supported by the project “BIOCEV—Biotechnology and Biomedicine Centre of the Academy of Sciences and Charles University" (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0109) from the European Regional Development Fund.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Vaccine preventable deaths and the Global Immunization Vision and Strategy, 2006-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2006;55:511–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raguckas SE, VandenBussche HL, Jacobs C, Klepser ME. Pertussis resurgence: diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and beyond. Pharmacotherapy. 2007;27:41–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Gent M, Heuvelman CJ, van der Heide HG, Hallander HO, Advani A, Guiso N, et al. Analysis of Bordetella pertussis clinical isolates circulating in European countries during the period 1998-2012. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:821–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fabiánová K, Benes C, Kríz B. A steady rise in incidence of pertussis since nineties in the Czech Republic. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 2010;59:25–33.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sealey KL, Belcher T, Preston A. Bordetella pertussis epidemiology and evolution in the light of pertussis resurgence. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;40:136–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Esposito S, Stefanelli P, Fry NK, Fedele G, He Q, Paterson P, et al.; World Association of Infectious Diseases and Immunological Disorders (WAidid) and the Vaccine Study Group of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (EVASG). (WAidid) and the Vaccine Study Group of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (EVASG). Pertussis prevention: reasons for resurgence, and differences in the current acellular pertussis vaccines. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1344. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cherry JD. Epidemic pertussis and acellular pertussis vaccine failure in the 21st century. Pediatrics. 2015;135:1130–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Klein NP, Bartlett J, Rowhani-Rahbar A, Fireman B, Baxter R. Waning protection after fifth dose of acellular pertussis vaccine in children. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1012–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liko J, Robison SG, Cieslak PR. Priming with whole-cell versus acellular pertussis vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:581–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burdin N, Handy LK, Plotkin SA. What is wrong with pertussis Vvccine immunity? The problem of waning effectiveness of pertussis vaccines. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9:
a029454 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Bart MJ, Harris SR, Advani A, Arakawa Y, Bottero D, Bouchez V, et al. Global population structure and evolution of Bordetella pertussis and their relationship with vaccination. MBio. 2014;5:
e01074 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Mooi FR, Van Der Maas NA, De Melker HE. Pertussis resurgence: waning immunity and pathogen adaptation - two sides of the same coin. Epidemiol Infect. 2014;142:685–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bouchez V, Hegerle N, Strati F, Njamkepo E, Guiso N. New data on vaccine antigen deficient Bordetella pertussis isolates. Vaccines (Basel). 2015;3:751–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, et al. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet. 2003;35:32–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cummings CA, Brinig MM, Lepp PW, van de Pas S, Relman DA. Bordetella species are distinguished by patterns of substantial gene loss and host adaptation. J Bacteriol. 2004;186:1484–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Linz B, Ivanov YV, Preston A, Brinkac L, Parkhill J, Kim M, et al. Acquisition and loss of virulence-associated factors during genome evolution and speciation in three clades of Bordetella species. BMC Genomics. 2016;17:767. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bowden KE, Weigand MR, Peng Y, Cassiday PK, Sammons S, Knipe K, et al. Genome structural diversity among 31 Bordetella pertussis isolates from two recent U.S. whooping cough statewide epidemics. MSphere. 2016;1:e00036–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Weigand MR, Peng Y, Loparev V, Batra D, Bowden KE, Burroughs M, et al. The history of Bordetella pertussis genome evolution includes structural rearrangement. J Bacteriol. 2017;199:e00806–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ring N, Abrahams JS, Jain M, Olsen H, Preston A, Bagby S. Resolving the complex Bordetella pertussis genome using barcoded nanopore sequencing. Microb Genom. 2018;4:4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brinig MM, Cummings CA, Sanden GN, Stefanelli P, Lawrence A, Relman DA. Significant gene order and expression differences in Bordetella pertussis despite limited gene content variation. J Bacteriol. 2006;188:2375–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Amman F, D’Halluin A, Antoine R, Huot L, Bibova I, Keidel K, et al. Primary transcriptome analysis reveals importance of IS elements for the shaping of the transcriptional landscape of Bordetella pertussis. RNA Biol. 2018;15:967–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dienstbier A, Pouchnik D, Wildung M, Amman F, Hofacker IL, Parkhill J, et al. Comparative genomics of Czech vaccine strains of Bordetella pertussis. Pathog Dis. 2018;76:76. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kasuga T, Nakase Y, Ukishima K, Takatsu K. Studies on Haemophilis pertussis. III. Some properties of each phase of H. pertussis. Kitasato Arch Exp Med. 1954;27:37–47.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stainer DW, Scholte MJ. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970;63:211–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT. progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One. 2010;5:
e11147 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hu F, Lin Y, Tang J. MLGO: phylogeny reconstruction and ancestral inference from gene-order data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15:354. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Angiuoli SV, Salzberg SL. Mugsy: fast multiple alignment of closely related whole genomes. Bioinformatics. 2011;27:334–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gardner SN, Slezak T, Hall BG. kSNP3.0: SNP detection and phylogenetic analysis of genomes without genome alignment or reference genome. Bioinformatics. 2015;31:2877–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):
W242-5 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Sealey KL, Harris SR, Fry NK, Hurst LD, Gorringe AR, Parkhill J, et al. Genomic analysis of isolates from the United Kingdom 2012 pertussis outbreak reveals that vaccine antigen genes are unusually fast evolving. J Infect Dis. 2015;212:294–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Block DH, Hussein R, Liang LW, Lim HN. Regulatory consequences of gene translocation in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40:8979–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Gouw D, Hermans PW, Bootsma HJ, Zomer A, Heuvelman K, Diavatopoulos DA, et al. Differentially expressed genes in Bordetella pertussis strains belonging to a lineage which recently spread globally. PLoS One. 2014;9:
e84523 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - King AJ, van der Lee S, Mohangoo A, van Gent M, van der Ark A, van de Waterbeemd B. Genome-wide gene expression analysis of Bordetella pertussis isolates associated with a resurgence in pertussis: elucidation of factors involved in the increased fitness of epidemic strains. PLoS One. 2013;8:
e66150 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Kang Y, Gu C, Yuan L, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Li X, et al. Flexibility and symmetry of prokaryotic genome rearrangement reveal lineage-associated core-gene-defined genome organizational frameworks. MBio. 2014;5:
e01867 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Dorman CJ. Genome architecture and global gene regulation in bacteria: making progress towards a unified model? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:349–55. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bryant JA, Sellars LE, Busby SJ, Lee DJ. Chromosome position effects on gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:11383–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kallonen T, Gröndahl-Yli-Hannuksela K, Elomaa A, Lutyńska A, Fry NK, Mertsola J, et al. Differences in the genomic content of Bordetella pertussis isolates before and after introduction of pertussis vaccines in four European countries. Infect Genet Evol. 2011;11:2034–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- West NP, Jungnitz H, Fitter JT, McArthur JD, Guzmán CA, Walker MJ. Role of phosphoglucomutase of Bordetella bronchiseptica in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis and virulence. Infect Immun. 2000;68:4673–80. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ugalde JE, Czibener C, Feldman MF, Ugalde RA. Identification and characterization of the Brucella abortus phosphoglucomutase gene: role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence and intracellular multiplication. Infect Immun. 2000;68:5716–23. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hardy GG, Magee AD, Ventura CL, Caimano MJ, Yother J. Essential role for cellular phosphoglucomutase in virulence of type 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 2001;69:2309–17. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tung SY, Kuo TT. Requirement for phosphoglucose isomerase of Xanthomonas campestris in pathogenesis of citrus canker. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:5564–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoffman CL, Gonyar LA, Zacca F, Sisti F, Fernandez J, Wong T, et al. Bordetella pertussis can be motile and express flagellum-like structures. MBio. 2019;10:e00787–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- van Beek LF, de Gouw D, Eleveld MJ, Bootsma HJ, de Jonge MI, Mooi FR, et al. Adaptation of Bordetella pertussis to the respiratory tract. J Infect Dis. 2018;217:1987–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wong TY, Hall JM, Nowak ES, Boehm DT, Gonyar LA, Hewlett EL, et al. Analysis of the in vivo transcriptome of Bordetella pertussis during infection of mice. MSphere. 2019;4:e00154–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Neo Y, Li R, Howe J, Hoo R, Pant A, Ho S, et al. Evidence for an intact polysaccharide capsule in Bordetella pertussis. Microbes Infect. 2010;12:238–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hoo R, Lam JH, Huot L, Pant A, Li R, Hot D, et al. Evidence for a role of the polysaccharide capsule transport proteins in pertussis pathogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9:
e115243 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Ada G, Isaacs D. Carbohydrate-protein conjugate vaccines. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2003;9:79–85. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fennelly NK, Sisti F, Higgins SC, Ross PJ, van der Heide H, Mooi FR, et al. Bordetella pertussis expresses a functional type III secretion system that subverts protective innate and adaptive immune responses. Infect Immun. 2008;76:1257–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaillard ME, Bottero D, Castuma CE, Basile LA, Hozbor D. Laboratory adaptation of Bordetella pertussis is associated with the loss of type three secretion system functionality. Infect Immun. 2011;79:3677–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Caro V, Bouchez V, Guiso N. Is the Sequenced Bordetella pertussis strain Tohama I representative of the species? J Clin Microbiol. 2008;46:2125–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Tables
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: December 15, 2020
Table of Contents – Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|


Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Branislav Večerek, Institute of Microbiology, Czech Academy of Sciences, Videnska 1083, 14220 Prague 4, Czech Republic
Top