IgG Seroconversion and Pathophysiology in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection
Henry M. Staines
1, Daniela E. Kirwan
1, David J. Clark
1, Emily R. Adams, Yolanda Augustin, Rachel L. Byrne, Michael Cocozza, Ana I. Cubas-Atienzar, Luis E. Cuevas, Martina Cusinato, Benedict M.O. Davies, Mark Davis, Paul Davis, Annelyse Duvoix, Nicholas M. Eckersley, Daniel Forton, Alice J. Fraser, Gala Garrod, Linda Hadcocks, Qinxue Hu, Michael Johnson, Grant A. Kay, Kesja Klekotko, Zawditu Lewis, Derek C. Macallan, Josephine Mensah-Kane, Stefanie Menzies, Irene Monahan, Catherine M. Moore, Gerhard Nebe-von-Caron, Sophie I. Owen, Chris Sainter, Amadou A. Sall, James Schouten, Christopher T. Williams, John Wilkins, Kevin Woolston, Joseph R.A. Fitchett, Sanjeev Krishna
2
, and Tim Planche
2
Author affiliations: St. George’s, University of London, London, UK (H.M. Staines, D.E. Kirwan, D.J. Clark, Y. Augustin, M. Cuisinato, B.M.O. Davies, N.M. Eckersley, D. Forton, L. Hadcocks, Q. Hu, D.C. Macallan, I. Monahan, C.M. Moore, S. Krishna, T. Planche); Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, Liverpool, UK (E.R. Adams, R.L. Byrne, A.I. Cubas-Atienzar, L.E. Cuevas, A.J. Fraser, G. Garrod, G.A. Kay, S. Menzies, S.I. Owen, C.T. Williams); Mologic, Thurleigh, UK (M. Cocozza, M. Davis, P. Davis, A. Duvoix, M. Johnson, K. Klekotko, Z. Lewis, J. Mensah-Kane, G. Nebe-von-Caron, C. Sainter, J. Schouten, J. Wilkins, K. Woolston, J.R.A. Fitchett); St. George’s University Hospitals National Health Services Foundation Trust, London (D. Forton, S. Krishna, T. Planche); Institut Pasteur, Dakar, Senegal (A.A. Sall); Universitätsklinikum Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany (S. Krishna); Centre de Recherches Médicales de Lambaréné, Lambaréné, Gabon (S. Krishna)
Main Article
Figure 2
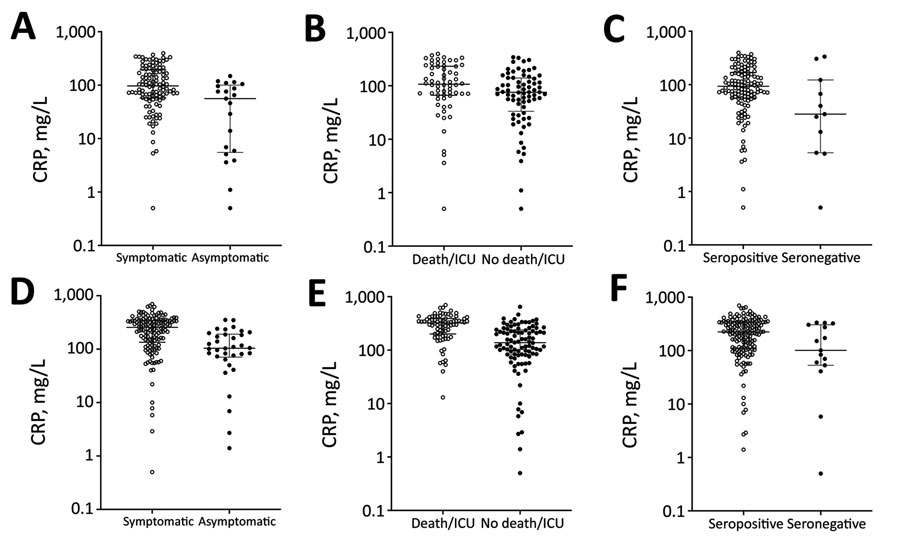
Figure 2. Relationships between CRP levels, symptoms, outcomes, and NODs of patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, United Kingdom, 2020. A–C) CRPs at diagnosis for A) 113 symptomatic (open circles) and 21 asymptomatic (closed circles) patients (CRP 97 vs. 56; p<0.01); B) 62 patients admitted to intensive care and/or who died (open circles) and 72 who were not admitted to intensive care (closed circles) (CRP 107 vs. 75.5; p = 0.01); C) 123 patients who seroconverted (open circles) and 11 who did not (closed circles) (CRP 93 vs. 28; p = 0.04). D–F) Peak CRPs corresponding to the populations in A–C: D) 255 (n = 142) vs. 104 (n = 34) (p<0.01); E) 322 (n = 80) vs. 137.5 (n = 96) (p<0.01); F) 224 (n = 161) vs. 101 (n = 15) (p = 0.03). Statistical significance calculated using Mann-Whitney test for CRPs (mg/L). CRP, C-reactive protein; NOD, normalized optical density.
Main Article
Page created: October 17, 2020
Page updated: December 21, 2020
Page reviewed: December 21, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
