Volume 27, Number 1—January 2021
Research
Cellular Immunity in COVID-19 Convalescents with PCR-Confirmed Infection but with Undetectable SARS-CoV-2–Specific IgG
Figure 3
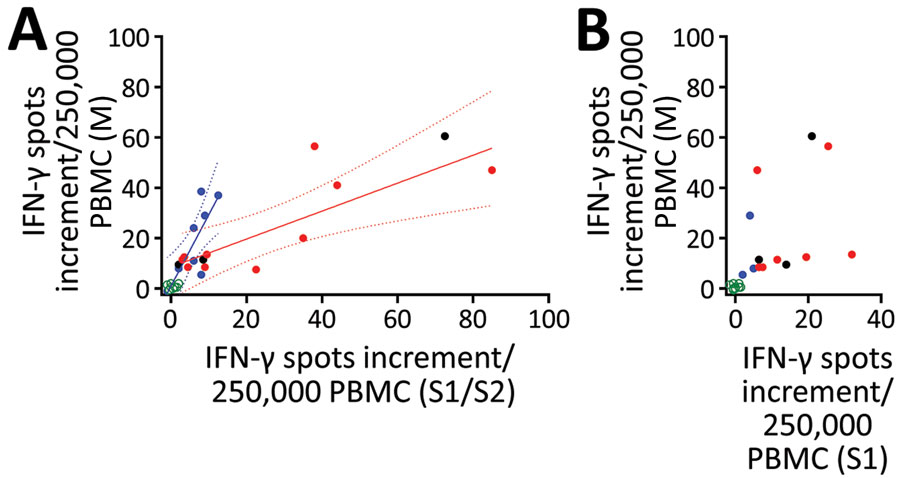
Figure 3. Interrelationship between results of various severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)–specific cellular assays in 78 potential convalescent-plasma donors with PCR-confirmed infection, Germany. The plots include the first dataset in potential convalescent plasma donors and in negative controls. Red dots represent volunteers with an antibody ratio >3; black dots, volunteers with a ratio of 1.1–3; blue dots, volunteers with ratio <1.1; green dots, NC. PBMCs of volunteers were stimulated by peptide pools of the S1/S2 and the M protein and by an S1 protein antigen of SARS-CoV-2. A) Analysis of ELISpot assay with S1/S2 peptides versus M peptides. We performed 2 linear regression analyses separately for potential plasma donors with an IgG ratio >3 and <1.1. Solid lines show regression lines and dotted lines 95% CI. B) Analysis of ELISpot assay with S1 protein versus M peptides. ELISpot, enzyme-linked immunospot; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells.