Volume 28, Number 2—February 2022
Research
Wild Boars as Reservoir of Highly Virulent Clone of Hybrid Shiga Toxigenic and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Responsible for Edema Disease, France
Figure 2
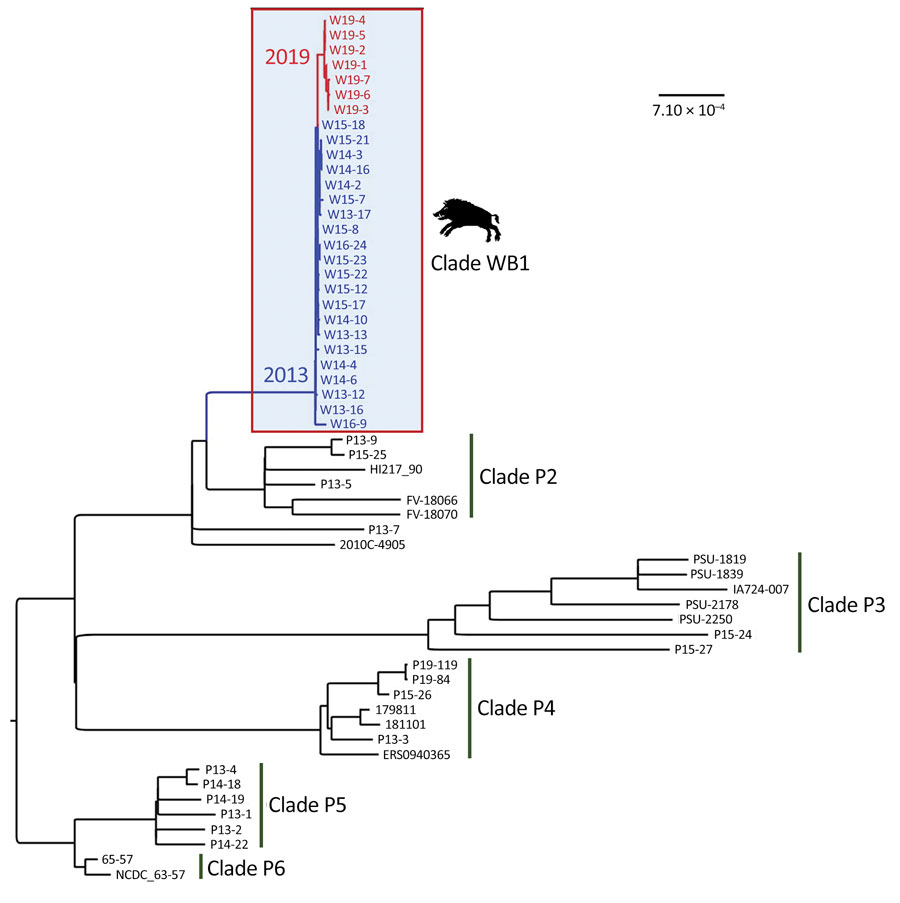
Figure 2. Core genome maximum-likelihood phylogenetic tree of 63 Escherichia coli O139:H1 (ST1) isolates from edema disease cases, including 28 from wild boars in France and 35 from domestic pigs of worldwide origin, including France. The clade of wild boar strains (WB1) is boxed, and the strains from this clade are colored according to the year of isolation (blue, 2013–2016; red, 2019). The clades of pig strains are numbered from P2 to P6. Scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site.
Page created: December 01, 2021
Page updated: January 27, 2022
Page reviewed: January 27, 2022
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.