Volume 28, Number 2—February 2022
Research
Genetic Relatedness of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus Isolates, United States, 2019
Figure 2
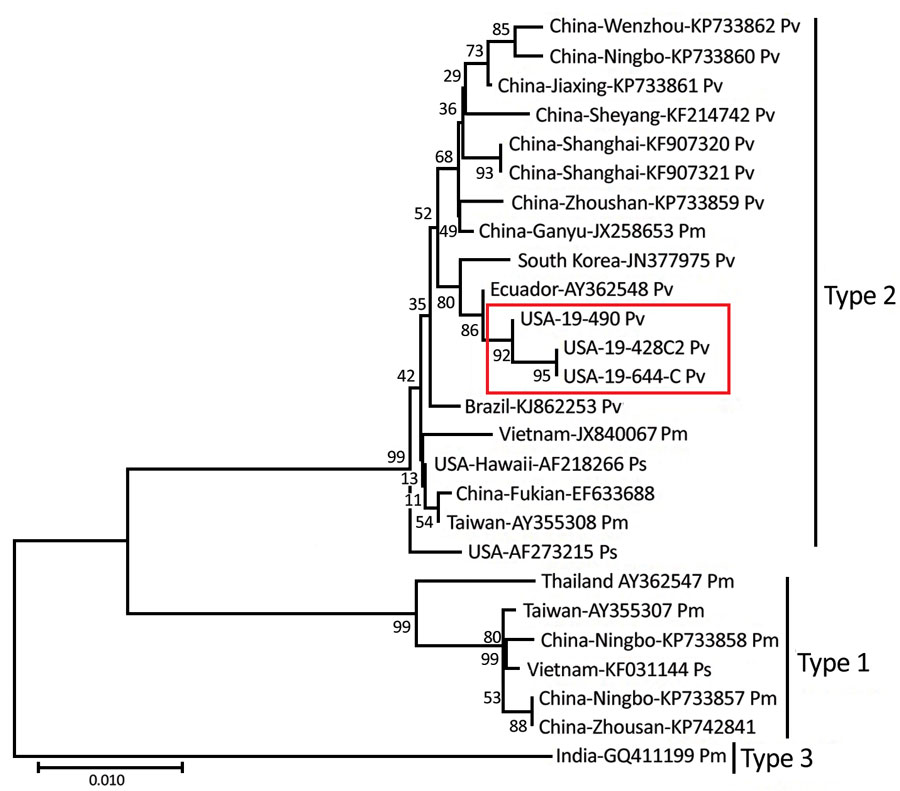
Figure 2. Evolutionary relationships of the infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) strains (19-428, 19-490, and 19-644) recently detected in the United States and published capsid protein gene sequences. The recent IHHNV strains (red box) fall into the type 2 lineage. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the neighbor-joining method (24). The optimal tree with the sum of branch length = 0.20086053 is shown. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths in the same units as those of the evolutionary distances used to infer the phylogenetic tree. The evolutionary distances were computed by using the maximum-likelihood method (25). Based upon full-genome phylogenetic analysis, the Texas and Florida IHHNV viruses appear to be related to a strain from Ecuador (GenBank accession no. AY362548.1). Scale bar indicates substitutions per site.
References
- Tijssen P, Agbandje-McKenna M, Almendral J, Bergoin M, Flegel T, Hedman K, et al. Parvoviridae. In: Murphy FA, Fauquet C, Bishop D, editors. Virus taxonomy: ninth report of the international committee on taxonomy of viruses. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2012. p. 405–25.
- Pénzes JJ, Pham HT, Chipman P, Bhattacharya N, McKenna R, Agbandje-McKenna M, et al. Molecular biology and structure of a novel penaeid shrimp densovirus elucidate convergent parvoviral host capsid evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117:20211–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shike H, Dhar AK, Burns JC, Shimizu C, Jousset FX, Klimpel KR, et al. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus of shrimp is related to mosquito brevidensoviruses. Virology. 2000;277:167–77. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dhar AK, Robles-Sikisaka R, Saksmerprome V, Lakshman DK. Biology, genome organization, and evolution of parvoviruses in marine shrimp. In: Advances in virus research, 1st ed. Amsterdam: Elsevier Inc.; 2014. p. 85–139.
- Lightner DV, Redman RM, Bell T, Brock J. Detection of IHHN virus in Penaeys stylirostris and P. vannamei imported into Hawaii. J World Maric Soc. 1983;225:212–25.
- Bell TA, Lightner DV. IHHN virus: Infectivity and pathogenicity studies in Penaeus stylirostris and Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture. 1984;38:185–94. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Dhar AK, Cruz-Flores R, Caro LFA, Siewiora HM, Jory D. Diversity of single-stranded DNA containing viruses in shrimp. Virusdisease. 2019;30:43–57. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Flegel TW. Detection of major penaeid shrimp viruses in Asia, a historical perspective with emphasis on Thailand. Aquaculture. 2006;258:1–33. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Sellars MJ, Cowley JA, Musson D, Rao M, Menzies ML, Coman GJ, et al. Reduced growth performance of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) infected with infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus. Aquaculture. 2019;499:160–6. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Centre for Environment Fisheries and Aquaculture Science. International database on aquatic animal disease: infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis, United Kingdom [Immediate notification 20/08/19]. 2019 [cited 2021 Jul 11]. https://www.cefas.co.uk/international-database-on-aquatic-animal-diseases/abstract/?id=1938
- Government of Canada. Fact sheet—infectious hypodermal and haematopoitic necrosis. 2019 [cited 2021 Jul 11]. https://inspection.canada.ca/animal-health/aquatic-animals/diseases/immediately-notifiable/infectious-hypodermal-and-haematopoitic-necrosis/eng/1562271424092/1562271424389#shr-pg0
- Tang KFJ, Lightner DV. Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV)-related sequences in the genome of the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon from Africa and Australia. Virus Res. 2006;118:185–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang KFJ, Navarro SA, Lightner DV. PCR assay for discriminating between infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) and virus-related sequences in the genome of Penaeus monodon. Dis Aquat Organ. 2007;74:165–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Durand SV, Lightner DV. Quantitative real time PCR for the measurement of white spot syndrome virus in shrimp. J Fish Dis. 2002;25:381–9. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Aranguren LF, Tang KFJ, Lightner DV. Quantification of the bacterial agent of necrotizing hepatopancreatitis (NHP-B) by real-time PCR and comparison of survival and NHP load of two shrimp populations. Aquaculture. 2010;307:187–92. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Tang KFJ, Pantoja CR, Redman RM, Han JE, Tran LH, Lightner DV. Development of in situ hybridization and PCR assays for the detection of Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei (EHP), a microsporidian parasite infecting penaeid shrimp. J Invertebr Pathol. 2015;130:37–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Han JE, Tang KF, Tran LH, Lightner DV. Photorhabdus insect-related (Pir) toxin-like genes in a plasmid of Vibrio parahaemolyticus, the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) of shrimp. Dis Aquat Organ. 2015;113:33–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Aranguren LF, Tang KFJ, Lightner DV. Protection from yellow head virus (YHV) infection in Penaeus vannamei pre-infected with Taura syndrome virus (TSV). Dis Aquat Organ. 2012;98:185–92. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tang KFJ, Wang J, Lightner DV. Quantitation of Taura syndrome virus by real-time RT-PCR with a TaqMan assay. J Virol Methods. 2004;115:109–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Andrade TPD, Srisuvan T, Tang KFJ, Lightner DV. Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay using TaqMan probe for detection and quantification of infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV). Aquaculture. 2007;264:9–15. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Robles-Sikisaka R, Bohonak AJ, McClenaghan LR Jr, Dhar AK. Genetic signature of rapid IHHNV (infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus) expansion in wild Penaeus shrimp populations. PLoS One. 2010;5:
e11799 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, et al. Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics. 2012;28:1647–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Nei M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol. 1993;10:512–26.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. 2016;33:1870–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaufmann B, Bowman VD, Li Y, Szelei J, Waddell PJ, Tijssen P, et al. Structure of Penaeus stylirostris densovirus, a shrimp pathogen. J Virol. 2010;84:11289–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nunan LM, Poulos BT, Lightner DV. Use of polymerase chain reaction for the detection of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus in Penaeid shrimp. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2000;2:319–28. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Saksmerprome V, Jitrakorn S, Chayaburakul K, Laiphrom S, Boonsua K, Flegel TW. Additional random, single to multiple genome fragments of Penaeus stylirostris densovirus in the giant tiger shrimp genome have implications for viral disease diagnosis. Virus Res. 2011;160:180–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). Infection with infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus. In: Manual of diagnostic tests for aquatic animals, 4th ed. Paris, France: Office International des Epizooties; 2017. p. 1–18.
- Senapin S, Phewsaiya K, Briggs M, Flegel TW. Outbreaks of infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV) in Indonesia confirmed by genome sequencing and use of an alternative RT-PCR detection method. Aquaculture. 2007;266:32–8. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Dhar AK, Lakshman DK, Amundsen K, Robles-Sikisaka R, Kaizer KN, Roy S, et al. Characterization of a Taura syndrome virus isolate originating from the 2004 Texas epizootic in cultured shrimp. Arch Virol. 2010;155:315–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chaijarasphong T, Thammachai T, Itsathitphaisarn O, Sritunyalucksana K, Suebsing R. Potential application of CRISPR-Cas12a fluorescence assay coupled with rapid nucleic acid amplification for detection of white spot syndrome virus in shrimp. Aquaculture. 2019;512:
734340 . DOIGoogle Scholar - Sullivan TJ, Dhar AK, Cruz-Flores R, Bodnar AG. Rapid, CRISPR-based, field-deployable detection of white spot syndrome virus in shrimp. Sci Rep. 2019;9:19702. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lightner V. Biosecurity in shrimp farming: pathogen exclusion through use of SPF stock and routine surveillance. J World Aquacult Soc. 2005;36:230–48. DOIGoogle Scholar