Volume 28, Number 6—June 2022
Research
Geographic Origin and Vertical Transmission of Leishmania infantum Parasites in Hunting Hounds, United States
Figure 6
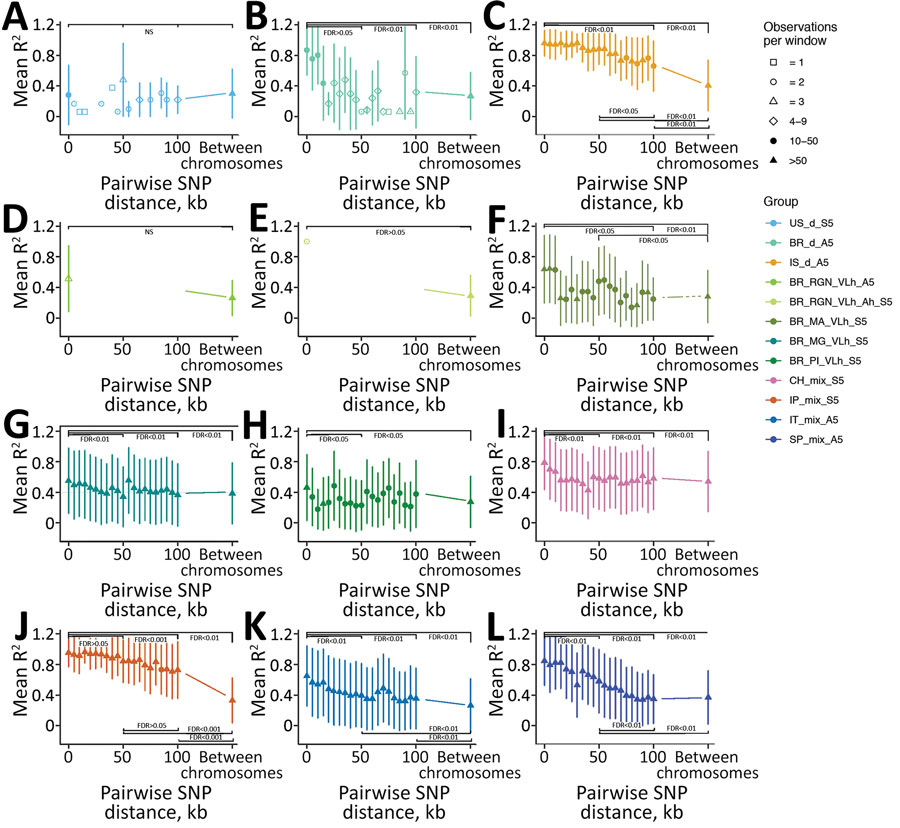
Figure 6. Decay of linkage disequilibrium with genomic distance across geographically confined groups of Leishmania infantum isolates. A) US_d_S5, B) BR_d_A5, C) IS_d_A5, D) BR_RGN_VLh_A5, E) BR_RGN_VLh_Ah_S5, F) BR_MA_VLh_Ah_S5, G) BR_MG_VLh_S5. H) BR_PI_VLh_S5, I) CH_mix_S5, J) IP_mix_A5, K) IT_mix_A5, L) SP_mix_A5. Long-range linkage disequilibrium was measured as R2 for pairs of SNPs up to 100 kb apart within chromosomes and located on different chromosomes. Symbols show mean R2 across SNP-pairs on all chromosomes, and lines show 1 SD for variants in bins of 5kb distance starting at the indicated distance. For groups with >5 samples, 5 have been randomly chosen to calculate R2 values, indicated in group names for each subplot (S6, subsampled 5; A5, all 5 samples of the group were used). Symbol shapes indicates the number of pairwise comparisons available for each distance bin. Statistical significance of comparisons between R2 between 4 different 5 kb windows at 0–4999 bp, 50–54.999 kb, 100–104.999 kb between SNP pairs for all between-chromosome comparisons are shown. FDR was determined based on the Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by the Dunn post hoc test when significant. For the groups in which only data for 2 of the 4 windows was present, the Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon test was used. FDR, false discovery rate; NS, not significant; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.