Volume 30, Number 7—July 2024
Research
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus Infection in Domestic Dairy Cattle and Cats, United States, 2024
Figure 1
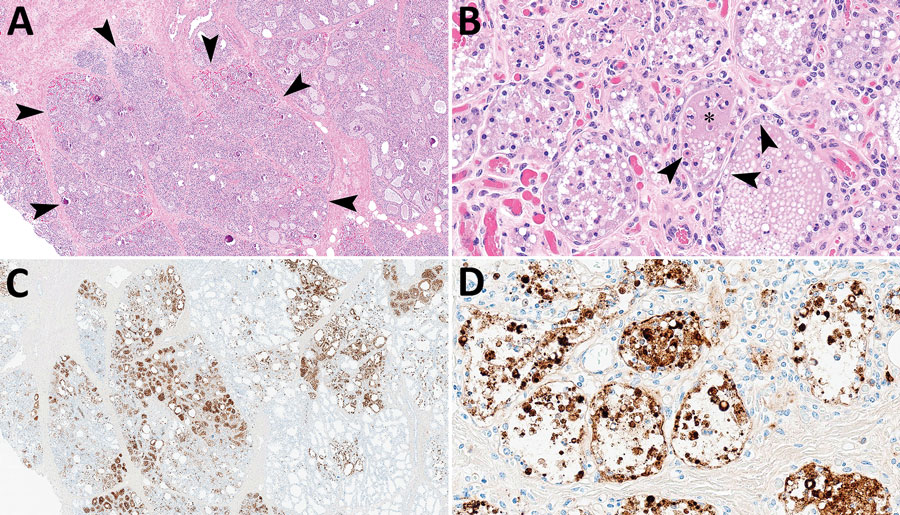
Figure 1. Mammary gland lesions in cattle in study of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus infection in domestic dairy cattle and cats, United States, 2024. A, B) Mammary gland tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin. A) Arrowheads indicate segmental loss within open secretory mammary alveoli. Original magnification ×40. B) Arrowheads indicate epithelial degeneration and necrosis lining alveoli with intraluminal sloughing. Asterisk indicates intraluminal neutrophilic inflammation. Original magnification ×400. C, D) Mammary gland tissue sections stained by using avian influenza A immunohistochemistry. C) Brown staining indicates lobular distribution of avian influenza A virus. Original magnification ×40. D) Brown staining indicates strong nuclear and intracytoplasmic immunoreactivity of intact and sloughed epithelial cells within mammary alveoli. Original magnification ×400.