Volume 31, Number 2—February 2025
Research
Cyclospora Genotypic Variations and Associated Epidemiologic Characteristics, United States, 2018–2021
Figure 1
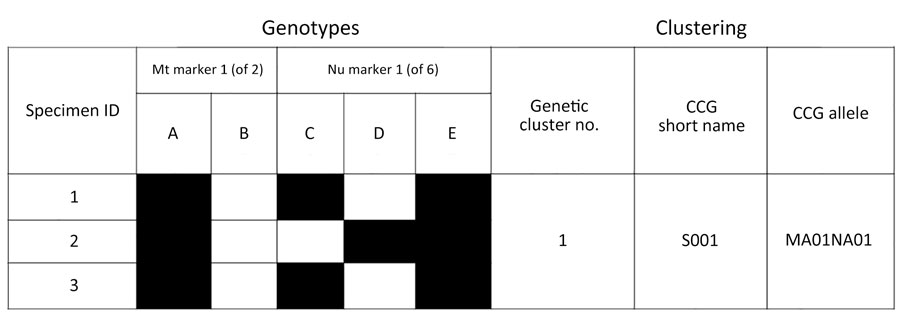
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a cluster consensus genotype in study of Cyclospora genotypic variations and associated epidemiologic characteristics United States, 2018–2021. Genotypes are derived from 8 markers, 2 Mt and 6 Nu; this schematic representation is based on 1 Mt and 1 Nu marker, where the haplotypes for this Mt marker are A or B, and the Nu haplotypes are C, D, or E. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Cyclospora genotyping system, Cybernetic Clustering Of Nonclonal Eukaryotes (CYCLONE) bioinformatic workflow, was used to determine the genetic similarity and clustered specimens 1, 2, and 3 in genetic cluster 1. Specimens 1 and 3 have genotype ACE, and specimen 2 has genotype ADE. Because genotype ACE is present in ≥50% of samples, it is the CCG for cluster 1, and its short name for this example is S001. The corresponding allele for this specific CCG is MA01 (Mt marker A) NA01 (Nu markers C and E). CCG, cluster consensus genotype; ID, identification; Mt, mitochondrial; Nu, nuclear.
1These senior authors were co–principal investigators.