Volume 17, Number 9—September 2011
Research
Classical Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy by Transmission of H-Type Prion in Homologous Prion Protein Context
Figure 1
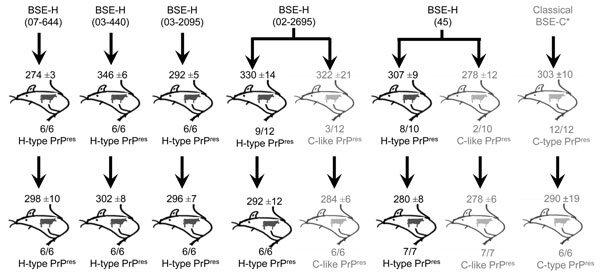
Figure 1. Overview of transmission of BSE-H isolates in tg110 mice. Five different isolates were intracerebrally inoculated into groups of 6–12 mice per isolate. Survival times at different serial passages are indicated as mean ± SD days postinoculation. Molecular profiles exhibited in the brains of inoculated mice are indicated as H-type, C-type, or C-like PrPres, and proportion of mice showing each profile. Previously reported data on BSE-C transmission in these mice (36) are included here only for comparison. BSE, bovine spongiform encephalitis; BSE-H, unglycosylated PrPres that is higher than BSE-C; H-type, high-type Western blot profile of PrPres; C-type, classical-type Western blot profile of PrPres; C-like, classical BSE–like; PrPres, protease-resistant prion protein; BSE-C, classical BSE.
References
- Dickinson AG, Meikle VM. Host-genotype and agent effects in scrapie incubation: change in allelic interaction with different strains of agent. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112:73–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Telling GC, Parchi P, DeArmond SJ, Cortelli P, Montagna P, Gabizon R, Evidence for the conformation of the pathologic isoform of the prion protein enciphering and propagating prion diversity. Science. 1996;274:2079–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hill AF, Desbruslais M, Joiner S, Sidle KC, Gowland I, Collinge J, The same prion strain causes vCJD and BSE. Nature. 1997;389:448–50, 526. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bruce M, Chree A, McConnell I, Foster J, Pearson G, Fraser H. Transmission of bovine spongiform encephalopathy and scrapie to mice: strain variation and the species barrier. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1994;343:405–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bruce ME, Will RG, Ironside JW, McConnell I, Drummond D, Suttie A, Transmissions to mice indicate that “new variant” CJD is caused by the BSE agent. Nature. 1997;389:498–501. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Aguzzi A, Glatzel M. Prion infections, blood and transfusions. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2006;2:321–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lasmézas CI, Deslys JP, Demaimay R, Adjou KT, Lamoury F, Dormont D, BSE transmission to macaques. Nature. 1996;381:743–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scott MR, Will R, Ironside J, Nguyen HO, Tremblay P, DeArmond SJ, Compelling transgenetic evidence for transmission of bovine spongiform encephalopathy prions to humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:15137–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ritchie DL, Boyle A, McConnell I, Head MW, Ironside JW, Bruce ME. Transmissions of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from brain and lymphoreticular tissue show uniform and conserved bovine spongiform encephalopathy–related phenotypic properties on primary and secondary passage in wild-type mice. J Gen Virol. 2009;90:3075–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Asante EA, Linehan JM, Desbruslais M, Joiner S, Gowland I, Wood AL, BSE prions propagate as either variant CJD-like or sporadic CJD-like prion strains in transgenic mice expressing human prion protein. EMBO J. 2002;21:6358–66. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Béringue V, Herzog L, Reine F, Le Dur A, Casalone C, Vilotte JL, Transmission of atypical bovine prions to mice transgenic for human prion protein. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1898–901. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wilesmith JW, Wells GA. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;172:21–38.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colchester AC, Colchester NT. The origin of bovine spongiform encephalopathy: the human prion disease hypothesis. Lancet. 2005;366:856–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jacobs JG, Langeveld JP, Biacabe AG, Acutis PL, Polak MP, Gavier-Widen D, Molecular discrimination of atypical bovine spongiform encephalopathy strains from a geographical region spanning a wide area in Europe. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:1821–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yamakawa Y, Hagiwara K, Nohtomi K, Nakamura Y, Nishijima M, Higuchi Y, Atypical proteinase K–resistant prion protein (PrPres) observed in an apparently healthy 23-month-old Holstein steer. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2003;56:221–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Masujin K, Shu Y, Yamakawa Y, Hagiwara K, Sata T, Matsuura Y, Biological and biochemical characterization of L-type-like bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) detected in Japanese black beef cattle. Prion. 2008;2:123–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Richt JA, Kunkle RA, Alt D, Nicholson EM, Hamir AN, Czub S, Identification and characterization of two bovine spongiform encephalopathy cases diagnosed in the United States. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2007;19:142–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dudas S, Yang J, Graham C, Czub M, McAllister TA, Coulthart MB, Molecular, biochemical and genetic characteristics of BSE in Canada. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e10638. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Buschmann A, Biacabe AG, Ziegler U, Bencsik A, Madec JY, Erhardt G, Atypical scrapie cases in Germany and France are identified by discrepant reaction patterns in BSE rapid tests. J Virol Methods. 2004;117:27–36. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Biacabe AG, Laplanche JL, Ryder S, Baron T. Distinct molecular phenotypes in bovine prion diseases. EMBO Rep. 2004;5:110–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Casalone C, Zanusso G, Acutis P, Ferrari S, Capucci L, Tagliavini F, Identification of a second bovine amyloidotic spongiform encephalopathy: molecular similarities with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:3065–70. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Capobianco R, Casalone C, Suardi S, Mangieri M, Miccolo C, Limido L, Conversion of the BASE prion strain into the BSE strain: the origin of BSE? PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Buschmann A, Gretzschel A, Biacabe AG, Schiebel K, Corona C, Hoffmann C, Atypical BSE in Germany—proof of transmissibility and biochemical characterization. Vet Microbiol. 2006;117:103–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Béringue V, Bencsik A, Le Dur A, Reine F, Lai TL, Chenais N, Isolation from cattle of a prion strain distinct from that causing bovine spongiform encephalopathy. PLoS Pathog. 2006;2:e112. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Béringue V, Andréoletti O, Le Dur A, Essalmani R, Vilotte JL, Lacroux C, A bovine prion acquires an epidemic bovine spongiform encephalopathy strain-like phenotype on interspecies transmission. J Neurosci. 2007;27:6965–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Castilla J, Gutiérrez-Adán A, Brun A, Pintado B, Ramirez MA, Parra B, Early detection of PrPres in BSE-infected bovine PrP transgenic mice. Arch Virol. 2003;148:677–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Manson JC, Clarke AR, Hooper ML, Aitchison L, McConnell I, Hope J. 129/Ola mice carrying a null mutation in PrP that abolishes mRNA production are developmentally normal. Mol Neurobiol. 1994;8:121–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Feraudet C, Morel N, Simon S, Volland H, Frobert Y, Creminon C, Screening of 145 anti-PrP monoclonal antibodies for their capacity to inhibit PrPSc replication in infected cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:11247–58. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yull HM, Ritchie DL, Langeveld JP, van Zijderveld FG, Bruce ME, Ironside JW, Detection of type 1 prion protein in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:151–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Andréoletti O, Lacroux C, Chabert A, Monnereau L, Tabouret G, Lantier F, PrPSc accumulation in placentas of ewes exposed to natural scrapie: influence of foetal PrP genotype and effect on ewe-to-lamb transmission. J Gen Virol. 2002;83:2607–16.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fraser H, Dickinson AG. The sequential development of the brain lesion of scrapie in three strains of mice. J Comp Pathol. 1968;78:301–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Andréoletti O, Simon S, Lacroux C, Morel N, Tabouret G, Chabert A, PrPSc accumulation in myocytes from sheep incubating natural scrapie. Nat Med. 2004;10:591–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Espinosa JC, Andréoletti O, Castilla J, Herva ME, Morales M, Alamillo E, Sheep-passaged bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent exhibits altered pathobiological properties in bovine-PrP transgenic mice. J Virol. 2007;81:835–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Castilla J, Gutiérrez-Adán A, Brun A, Pintado B, Parra B, Ramirez MA, Different behavior toward bovine spongiform encephalopathy infection of bovine prion protein transgenic mice with one extra repeat octapeptide insert mutation. J Neurosci. 2004;24:2156–64. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bruce ME, McConnell I, Fraser H, Dickinson AG. The disease characteristics of different strains of scrapie in Sinc congenic mouse lines: implications for the nature of the agent and host control of pathogenesis. J Gen Virol. 1991;72:595–603. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bishop MT, Hart P, Aitchison L, Baybutt HN, Plinston C, Thomson V, Predicting susceptibility and incubation time of human-to-human transmission of vCJD. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:393–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Padilla D, Béringue V, Espinosa JC, Andréoletti O, Jaumain E, Reine F, Sheep and goat BSE propagate more efficiently than cattle BSE in human PrP transgenic mice. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7:e1001319. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar