Volume 18, Number 1—January 2012
Research
Assessing Prion Infectivity of Human Urine in Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
Figure 1
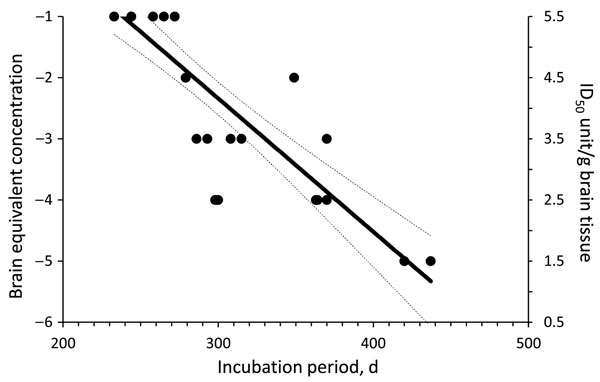
Figure 1. Dose-incubation period curve of brain microsomal fraction from sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease MM1 (patient 1) intracerebrally injected into Tg40 mice. Each solid circle represents the incubation time for single animal (x-axis) at different brain tissue equivalent dilution. Animals with the same incubation times have overlapping solid circles. Right y-axis is the amount of infectivity present in the inoculum at each brain tissue equivalent dilution (left y-axis). The experimental points were fitted by linear regression curve and 50% infectious dose (ID50) calculated by using probit-nonlinear regression analysis. Dashed lines indicate 95% confidence interval.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: December 22, 2011
Page updated: December 22, 2011
Page reviewed: December 22, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.