Volume 20, Number 1—January 2014
Research
Molecular Barriers to Zoonotic Transmission of Prions
Figure 1
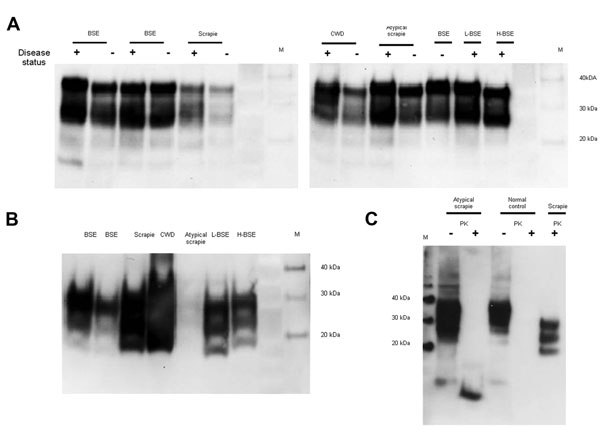
Figure 1. . Determination of total PrP and PrPres level in animal tissues. To characterize the PrP expression levels (total PrP), brain homogenates were analyzed by Western blot without digestion with PK. Nineteen microliters of each 10% wt/vol homogenate was loaded in each lane (A). To detect the PrPres in the samples, PK digestion (50 μg/mL) was performed to remove PrPC, and the samples were then reanalyzed (B). The atypical scrapie and matched normal control animal samples were further analyzed by Western blot both with (+) and without (–) prior PK digestion (C) by comparing 3 μL of undigested homogenates with 100 μL of the PK-digested sample concentrated by centrifugation. Five microliters of a PK-digested classical scrapie brain homogenate was analyzed in parallel for comparison. The detection antibody was 6H4 in (A) and (B) and 9A2 in (C). PrP, prion protein; PrPres, protease-resistant PrP; PK, proteinase K; PrPc, normal cellular PrP; M, molecular marker; BSE, bovine spongiform encephalopathy; +, animal prion disease sample; –, matched normal animal control sample; CWD, chronic wasting disease; L-BSE, L-type BSE; H-BSE, H-type BSE.