Volume 20, Number 10—October 2014
Research
Clinical Isolates of Shiga Toxin 1a–Producing Shigella flexneri with an Epidemiological Link to Recent Travel to Hispañiola
Figure 3
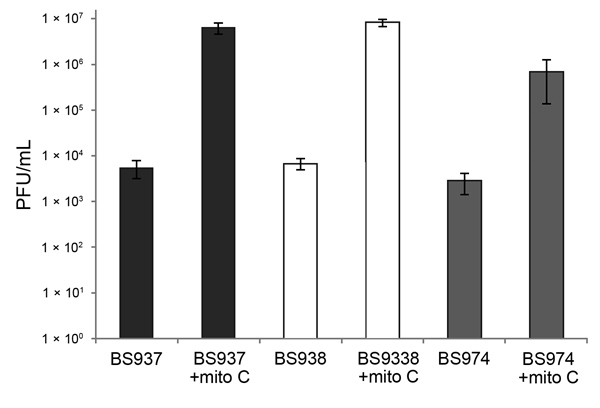
Figure 3. Infectious phage in the supernatants of Shiga toxin 1a gene (stx1a)–encoding Shigella flexneri are induced with mitomycin C (mito C) treatment. Supernatants were collected from exponential cultures of BS937, BS938, and BS974 grown with or without 0.5 μg/mL mito C for 3 h. The number of infectious phage particles was determined by a soft agar overlay method that used Escherichia coli MG1655 as the recipient. Plaque forming units (PFUs) of phage lysate were counted after 24 h incubation. Data are averages of 3 independent experiments. Error bars indicate standard error.
Page created: September 12, 2014
Page updated: September 12, 2014
Page reviewed: September 12, 2014
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.