Volume 23, Number 3—March 2017
Research
Zika Virus RNA Replication and Persistence in Brain and Placental Tissue
Figure 2
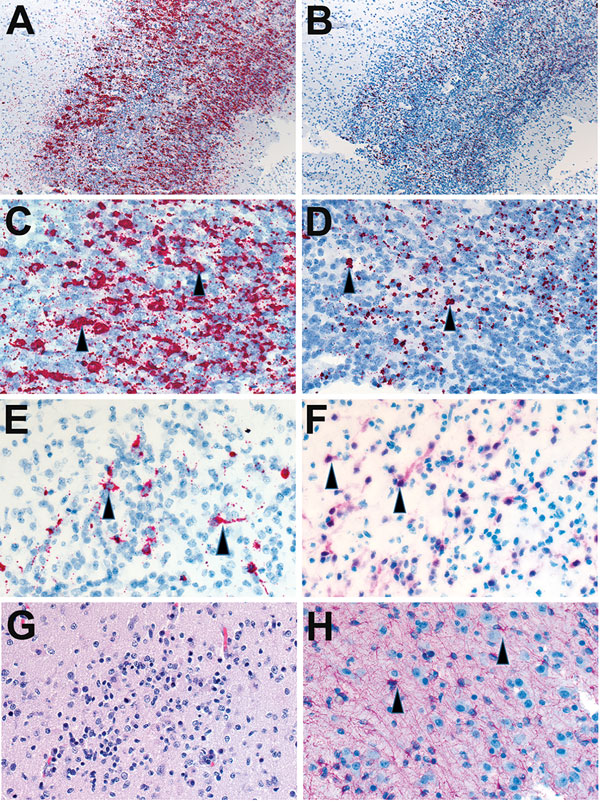
Figure 2. Localization of Zika virus RNA by in situ hybridization in brain tissues from infants with microcephaly. A) ISH with use of antisense probe. Zika virus genomic RNA (red stain) in cerebral cortex of an infant (case-patient no. 66, gestational age 26 wk). Original magnification ×10. B) ISH with use of sense probe. Serial section showing negative-strand replicative RNA intermediates (red stain) in the same areas shown in panel A. Original magnification ×10. C) ISH with use of antisense probe. Higher magnification of panel A, showing cytoplasmic staining of neural (arrowheads) and glial cells. Original magnification ×20. D) ISH with use of sense probe. Higher magnification of panel B, showing cytoplasmic staining of neural and glial cells (arrowheads). Original magnification ×20. E) ISH with use of antisense probe. Localization of negative-strand replicative RNA intermediates in neural cells or neurons (red, arrowheads) of another infant with fatal outcome (case-patient no. 67, gestational age 27 wk). Original magnification ×40. F) Immunostaining of neurons (arrowheads) with use of antibodies against neuronal nuclei in a serial section. Original magnification ×40. G) Hematoxylin and eosin stain showing cortical neural cells in a serial section. Original magnification ×40. H) Immunostaining of glial cells (arrowheads) with use of glial fibrillary acidic protein antibody in the same case. Original magnification ×40. ISH, in situ hybridization.