Variable Protease-Sensitive Prionopathy Transmission to Bank Voles
Romolo Nonno
1, Silvio Notari
1, Michele Angelo Di Bari, Ignazio Cali, Laura Pirisinu, Claudia d’Agostino, Laura Cracco, Diane Kofskey, Ilaria Vanni, Jody Lavrich, Piero Parchi, Umberto Agrimi, and Pierluigi Gambetti

Author affiliations: Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy (R. Nonno, M.A. Di Bari, L. Pirisinu, C. d’Agostino, I. Vanni, U. Agrimi); Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, USA (S. Notari, I. Cali, L. Cracco, D. Kofskey, J. Lavrich, P. Gambetti); University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy (P. Parchi); Istituto delle Scienze Neurologiche di Bologna, Bologna (P. Parchi)
Main Article
Figure 5
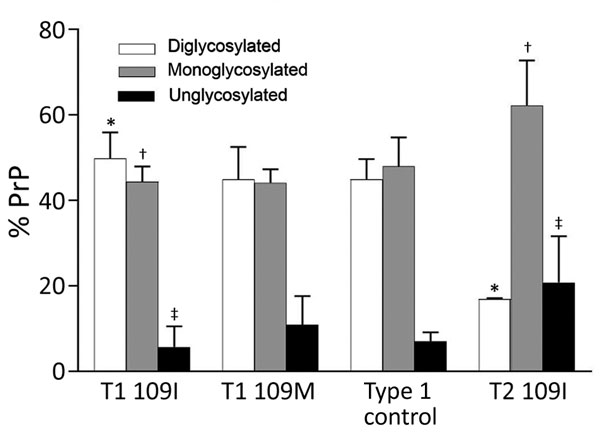
Figure 5. Glycoform ratio of protease-resistant, disease-related prion protein (resPrPD) in phenotypes T1 and T2. The ratio of resPrPD associated with T1 (T1 109I) was 48% for diglycosylated, 44% for monoglycosylated, and 8% for unglycosylated conformers and significantly differed in each glycoform from the 17%, 63%, and 20% corresponding ratio of T2 (T2 109I). *p<0.0001; †p<0.005; ‡p<0.05). Glycoform ratios of T1 109I and T1 109M as well as that of type 1 control (from bank voles 109I inoculated with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease MV1 and used as human type 1 controls) did not significantly differ from each other. Each bar represents mean ± SD of n = 4 for T1 109M, n = 6 for T1 109I, n = 6 for T2, and n = 2 for type 1 control.
Main Article
Page created: December 18, 2018
Page updated: December 18, 2018
Page reviewed: December 18, 2018
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
