Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2−Specific Antibody Responses in Coronavirus Disease Patients
Nisreen M.A. Okba
1, Marcel A. Müller
1, Wentao Li
1, Chunyan Wang, Corine H. GeurtsvanKessel, Victor M. Corman, Mart M. Lamers, Reina S. Sikkema, Erwin de Bruin, Felicity D. Chandler, Yazdan Yazdanpanah, Quentin Le Hingrat, Diane Descamps, Nadhira Houhou-Fidouh, Chantal B.E.M. Reusken, Berend-Jan Bosch, Christian Drosten, Marion P.G. Koopmans, and Bart L. Haagmans

Author affiliations: Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands (N.M.A. Okba, C.H. GeurtsvanKessel, M.M. Lamers, R.S. Sikkema, E. deBruin, F.D. Chandler, C.B.E.M. Reusken, M.P.G. Koopmans, B.L. Haagmans); Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Berlin, Germany (M.A. Müller, V.M. Corman, C. Drosten); German Centre for Infection Research, Berlin (M.A. Müller, V.M. Corman, C. Drosten); Utrecht University, Utrecht, the Netherlands (W. Li, C. Wang, B.-J. Bosch); Université de Paris, Paris, France (Y. Yazdanpanah, Q. Le Hingrat, D. Descamps); Hôpital Bichat-Claude Bernard, Paris (Y. Yazdanpanah, Q. Le Hingrat, D. Descamps, N. Houhou-Fidouh); RIVM, Bilthoven, the Netherlands (C.B.E.M. Reusken)
Main Article
Figure 1
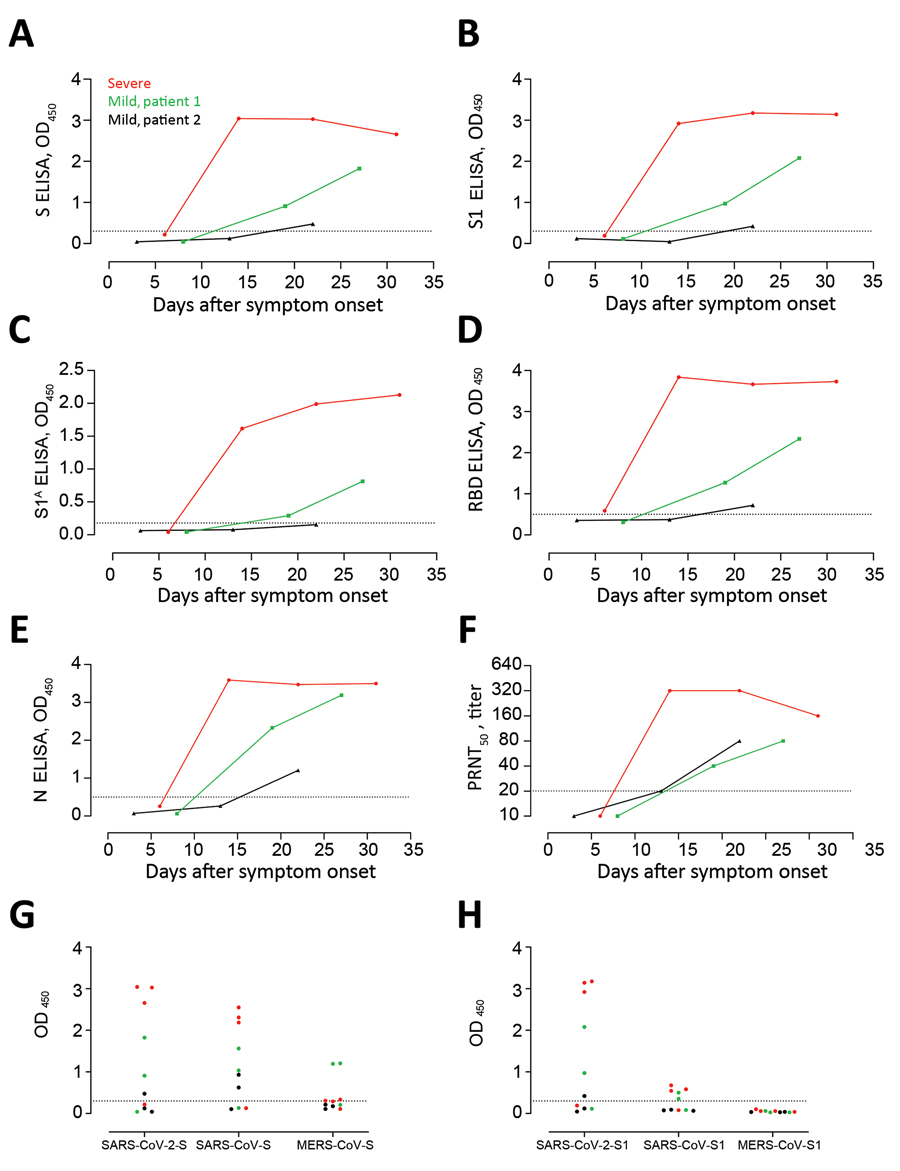
Figure 1. Kinetics of antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 after infection. We tested 1 patient who had severe coronavirus disease 2019 (red) and 2 patients who had mild coronavirus disease 2019 (green and black) for antibody responses against A) S protein, B) S protein S1 subunit, C) S N-terminal (S1A) domain, D) RDB, and E) N protein by using ELISAs. F) Virus-neutralizing antibodies were tested by using a PRNT50. G, H) Reactivities of serum samples from the 3 patients at different time points against whole S (G) and S1 (H) of SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV were tested by ELISAs. Dotted horizontal lines indicate ELISA cutoff values. MERS-CoV, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; N, nucleocapsid; OD, optical density; PRNT50, 50% plaque reduction neutralization test; RBD, receptor-binding domain; S, spike; SARS-CoV, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Main Article
Page created: April 08, 2020
Page updated: June 18, 2020
Page reviewed: June 18, 2020
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
