Volume 27, Number 9—September 2021
Research
Reduction in Antimicrobial Use and Resistance to Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Escherichia coli in Broiler Chickens, Canada, 2013–2019
Figure 5
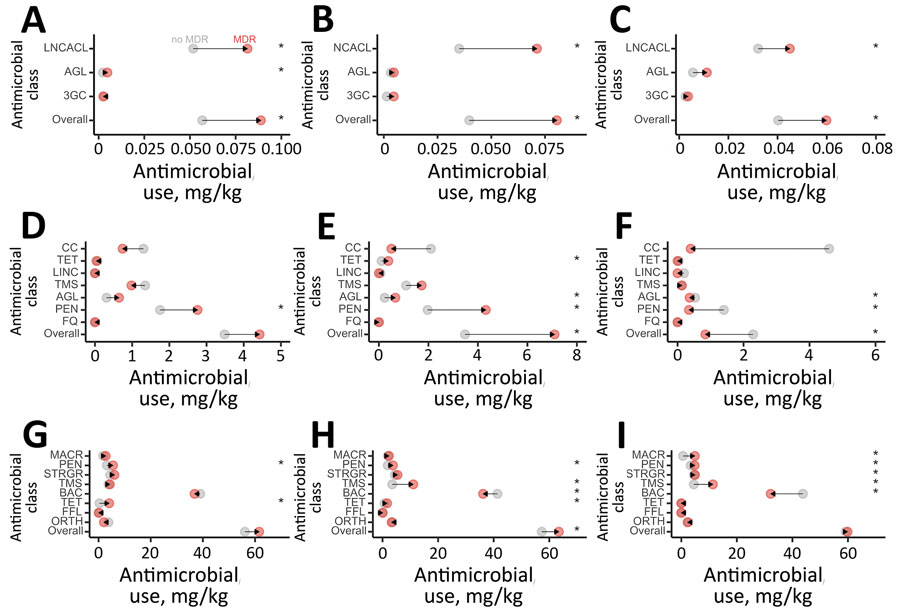
Figure 5. Mean antimicrobial use through injection, water, and feed in broiler chicken flocks where Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Campylobacter were isolated, Canada, 2013–2019. A) Salmonella; B) Escherichia coli; C) Campylobacter. Route of administration in each panel: top, in ovo or subcutaneous injections; middle, water; bottom, feed. Arrows represent directionality from no multidrug resistance (MDR; gray) to MDR (red). Asterisks (*) indicates p<0.05, obtained from mixed effects logistic regression including antimicrobial use as fixed effect and flock and veterinarian identification as random effects. AGL, aminoglycoside; BAC, bacitracin; CC, chemical coccidiostats; FFL, flavophospholipid; FQ, fluoroquinolone; LINC, lincomycin; LNCACL, lincosamides; MACR, macrolide; ORTH, orthomycin; PEN, penicillin; STRGR, streptogramin; TET, tetracycline; TMS, trimethropim-sulfonamides; 3GC, third-generation cephalosporin.