Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Research
Lack of Transmission of Chronic Wasting Disease Prions to Human Cerebral Organoids
Figure 3
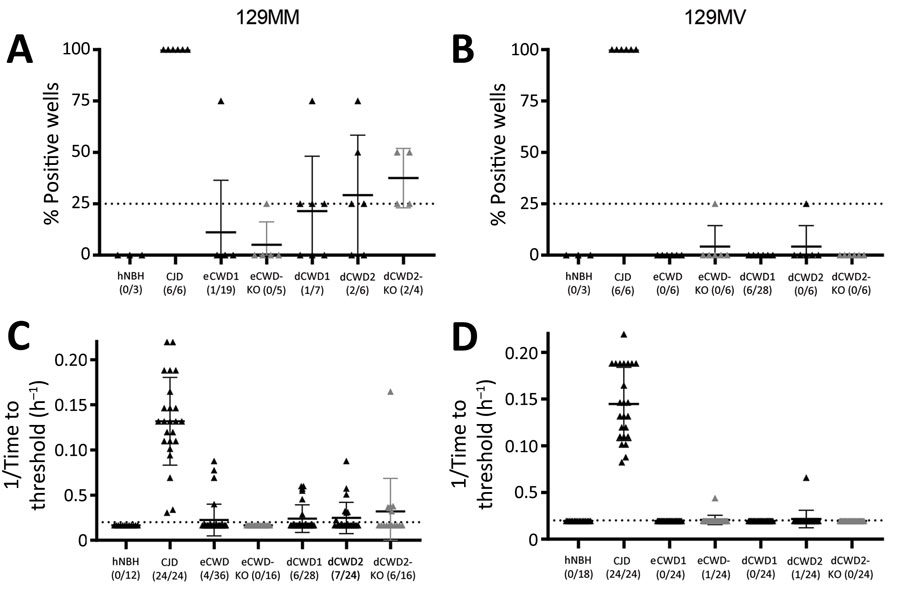
Figure 3. Real-time quaking-induced conversion (RT-QuIC) seeding activity of CWD-exposed organoids in study of lack of transmission of chronic wasting disease prions to human cerebral organoids. RT-QuIC seeding activity in organoids harvested at 180 days postinoculation is shown as either % positive wells (A, B) or the reciprocal of time-to-significance threshold (C, D) for the 129MM (A, C) and 129MV (B, D) organoids. Dotted lines indicate the threshold above which a sample would be classified as positive. Individual dots show single organoids with the means and SDs indicated. Gray symbols are indicative of knockout organoids. No significant differences were observed between the CWD-inoculated wild type organoids and their corresponding knockout organoids by Welch’s t-test. CJD, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease; CWD, chronic wasting disease; dCWD1, whitetail deer CWD; dCWD2, mule deer CWD; dNBH, deer normal brain homogenate; eCWD, elk CWD; eNBH, elk normal brain homogenate; hNBH, human normal brain homogenate.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.