Volume 15, Number 9—September 2009
Research
Susceptibilities of Nonhuman Primates to Chronic Wasting Disease
Figure 4
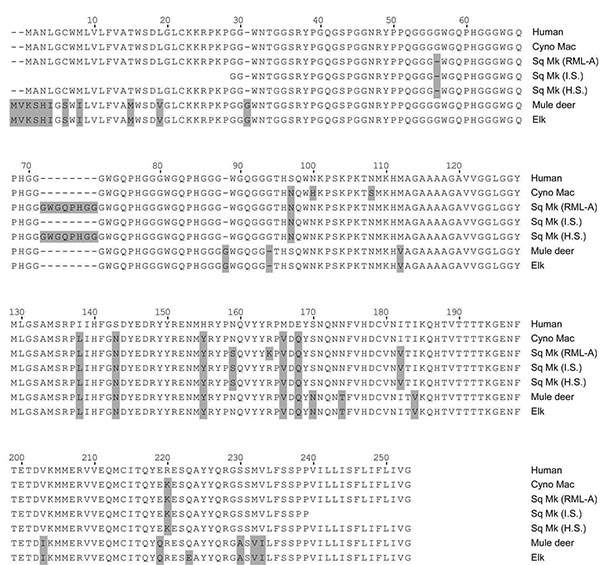
Figure 4. Comparison of prion protein sequences from various species. The following species are shown, and GenBank accession numbers are given when available: human (M13899), cynomolgus macaque (Cyno Mac) (U08298), squirrel monkey (Sq Mk) (genotype RML-A, see Table 4), squirrel monkey from Schneider et al. (31) (AY765385), squirrel monkey from Schätzl et al. (28) (U08310), mule deer (AY330343), and elk (AF156183). Numbering is based on the human sequence. Gray boxes indicate residues different from human residues. Alignment of the sequences was conducted with MegAlign software (DNAstar/Lasergene, Madison, WI, USA).
References
- Williams ES, Young S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: a spongiform encephalopathy. J Wildl Dis. 1980;16:89–98.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller MW, Williams ES. Chronic wasting disease of cervids. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;284:193–214.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamir AN, Kunkle RA, Cutlip RC, Miller JM, O’Rourke KI, Williams ES, Experimental transmission of chronic wasting disease agent from mule deer to cattle by the intracerebral route. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2005;17:276–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamir AN, Kunkle RA, Cutlip RC, Miller JM, Williams ES, Richt JA. Transmission of chronic wasting disease of mule deer to Suffolk sheep following intracerebral inoculation. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2006;18:558–65.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sigurdson CJ, Mathiason CK, Perrott MR, Eliason GA, Spraker TR, Glatzel M, Experimental chronic wasting disease (CWD) in the ferret. J Comp Pathol. 2008;138:189–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bartz JC, Marsh RF, McKenzie DI, Aiken JM. The host range of chronic wasting disease is altered on passage in ferrets. Virology. 1998;251:297–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harrington RD, Baszler TV, O’Rourke KI, Schneider DA, Spraker TR, Liggitt HD, A species barrier limits transmission of chronic wasting disease to mink (Mustela vison). J Gen Virol. 2008;89:1086–96. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raymond GJ, Raymond LD, Meade-White KD, Hughson AG, Favara C, Gardner D, Transmission and adaptation of chronic wasting disease to hamsters and transgenic mice: evidence for strains. J Virol. 2007;81:4305–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sigurdson CJ, Manco G, Schwarz P, Liberski P, Hoover EA, Hornemann S, Strain fidelity of chronic wasting disease upon murine adaptation. J Virol. 2006;80:12303–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kong Q, Huang S, Zou W, Vanegas D, Wang M, Wu D, Chronic wasting disease of elk: transmissibility to humans examined by transgenic mouse models. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7944–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamguney G, Giles K, Bouzamondo-Bernstein E, Bosque PJ, Miller MW, Safar J, Transmission of elk and deer prions to transgenic mice. J Virol. 2006;80:9104–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marsh RF, Kincaid AE, Bessen RA, Bartz JC. Interspecies transmission of chronic wasting disease prions to squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus). J Virol. 2005;79:13794–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brown P, Gibbs CJ Jr, Rodgers-Johnson P, Asher DM, Sulima MP, Bacote A, Human spongiform encephalopathy: the National Institutes of Health series of 300 cases of experimentally transmitted disease. Ann Neurol. 1994;35:513–29. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams L, Brown P, Ironside J, Gibson S, Will R, Ritchie D, Clinical, neuropathologial and immunohistochemical features of sporadic and variant forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the squirrel monkey (Saimiri scuireus). J Gen Virol. 2007;88:688–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lasmezas CI, Deslys JP, Demaimay R, Adjou KT, Lamoury F, Dormont D, BSE transmission to macaques. Nature. 1996;381:743–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hayasaka K, Gojobori T, Horai S. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of primate mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol. 1988;5:626–44.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Meade-White K, Race B, Trifilo M, Bossers A, Favara C, Lacasse R, Resistance to chronic wasting disease in transgenic mice expressing a naturally occurring allelic variant of deer prion protein. J Virol. 2007;81:4533–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sigurdson CJ, Williams ES, Miller MW, Spraker TR, O’Rourke KI, Hoover EA. Oral transmission and early lymphoid trophism of chronic wasting disease PrPres in mule deer fawns (Odocoileus hemionus). J Gen Virol. 1999;80:2757–64.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raymond GJ, Bossers A, Raymond LD, O’Rourke KI, McHolland LE, Bryant PK III, Evidence of a molecular barrier limiting susceptibility of humans, cattle and sheep to chronic wasting disease. EMBO J. 2000;19:4425–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scott MR, Kohler R, Foster D, Prusiner SB. Chimeric prion protein expression in cultured cells and transgenic mice. Protein Sci. 1992;1:986–97. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Race BL, Meade-White KD, Ward A, Jewell J, Miller MW, Williams ES, Levels of abnormal prion protein in deer and elk with chronic wasting disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:824–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kascsak RJ, Rubenstein R, Merz PA, Tonna-DeMasi M, Fersko R, Carp RI, Mouse monoclonal and polyclonal antibody to scrapie-associated fibril proteins. J Virol. 1987;61:3688–93.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Matsunaga Y, Peretz D, Williamson A, Burton D, Mehlhorn I, Groth D, Cryptic epitopes in N–terminally truncated prion protein are exposed in the full-length molecule: dependence of conformation on pH. Proteins. 2001;44:110–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vorberg I, Buschmann A, Harmeyer S, Saalmuller A, Pfaff E, Groschup MH. A novel epitope for the specific detection of exogenous prion proteins in transgenic mice and transfected murine cell lines. Virology. 1999;255:26–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Race B, Meade-White K, Oldstone MB, Race R, Chesebro B. Detection of prion infectivity in fat tissues of scrapie-infected mice. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000232. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kercher L, Favara C, Striebel JF, Lacasse R, Chesebro B. Prion protein expression differences in microglia and astroglia influence scrapie-induced neurodegenration in the retina and brain of transgenic mice. J Virol. 2007;81:10340–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schätzl HM, Da Costa M, Taylor L, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB. Prion protein variation among primates. J Mol Biol. 1995;245:362–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- O’Rourke KI, Spraker TR, Hamburg LK, Besser TE, Brayton KA, Knowles DP. Polymorphisms in prion precursor functional gene but not the pseudogene are associated with susceptibility to chronic wasting disease in white-tailed deer. J Gen Virol. 2004;85:1339–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fox KA, Jewell JE, Williams ES, Miller MW. Patterns of PrPCWD accumulation during the course of chronic wasting disease infection in orally inoculated mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus). J Gen Virol. 2006;87:3451–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schneider I, Schneider H, Schneider MP, Silva A. The prion protein and New World primate phylogeny. Genet Mol Biol. 2004;27:505–10. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Gibbs CJ Jr, Gajdusek DC. Experimental subacute spongiform virus encephalopathies in primates and other laboratory animals. Science. 1973;182:67–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spraker TR, Zink RR, Cummings BA, Wild MA, Miller MW, O’Rourke KI. Comparison of histological lesions and immunohistochemical staining of proteinease-resistant prion protein in a naturally occurring spongiform encephalopathy of free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with those of chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer. Vet Pathol. 2002;39:110–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Herzog C, Riviere J, Lescoutra-Etchegaray N, Charbonnier A, Leblanc V, Sales N, PrPTSE distribution in a primate model of variant, sporadic, and iatrogenic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Virol. 2005;79:14339–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lasmezas CI, Comoy E, Hawkins S, Herzog C, Mouthon F, Konold T, Risk of oral infection with bovine spongiform encephalopathy agent in primates. Lancet. 2005;365:781–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Belay ED, Maddox RA, Williams ES, Miller MW, Gambetti P, Schonberger LB. Chronic wasting disease and potential transmission to humans. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:977–84.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mawhinney S, Pape WJ, Forster JE, Anderson CA, Bosque P, Miller MW. Human prion disease and relative risk associated with chronic wasting disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1527–35.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Anderson CA, Bosque P, Filley CM, Arciniegas DB, Kleinschmidt-Demasters BK, Pape WJ, Colorado surveillance program for chronic wasting disease transmission to humans: lessons from 2 highly suspicious but negative cases. Arch Neurol. 2007;64:439–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 07, 2010
Page updated: December 07, 2010
Page reviewed: December 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.