Volume 23, Number 2—February 2017
Research
Swine Influenza Virus (H1N2) Characterization and Transmission in Ferrets, Chile
Figure 3
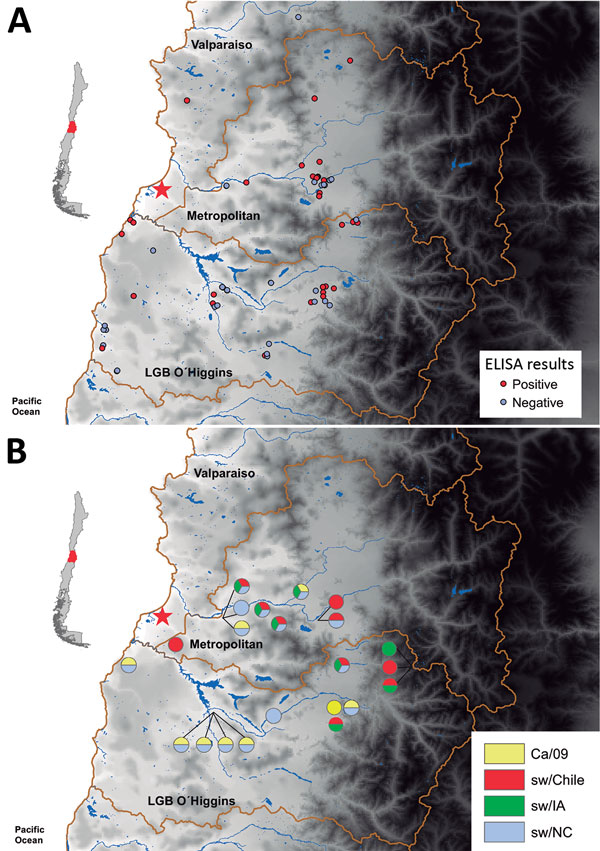
Figure 3. Testing for influenza in swine from backyard production farms (BPFs) in Central Chile. Swine serum samples collected from BPFs were analyzed for antibodies against influenza by nucleoprotein (NP)–specific ELISA, and hemagglutination inhibition analysis of serum samples from NP ELISA–positive farms was conducted to determine subtype. A) Results of influenza testing by BPF location. Red circles indicate location of positive farms, and gray circles indicate location of negative farms. B) Pie charts showing percentage of swine at each sampling site seropositive for each virus type: sw/Chile (red), CA/09 (yellow), sw/IA (green), and sw/NC (blue). Red star indicates location of sw/Chile H1N2 virus isolate. Insets indicate region of Central Chile covered by this study.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
2These senior authors contributed equally to this article.