Volume 30, Number 7—July 2024
Research
Sialic Acid Receptor Specificity in Mammary Gland of Dairy Cattle Infected with Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus
Figure 4
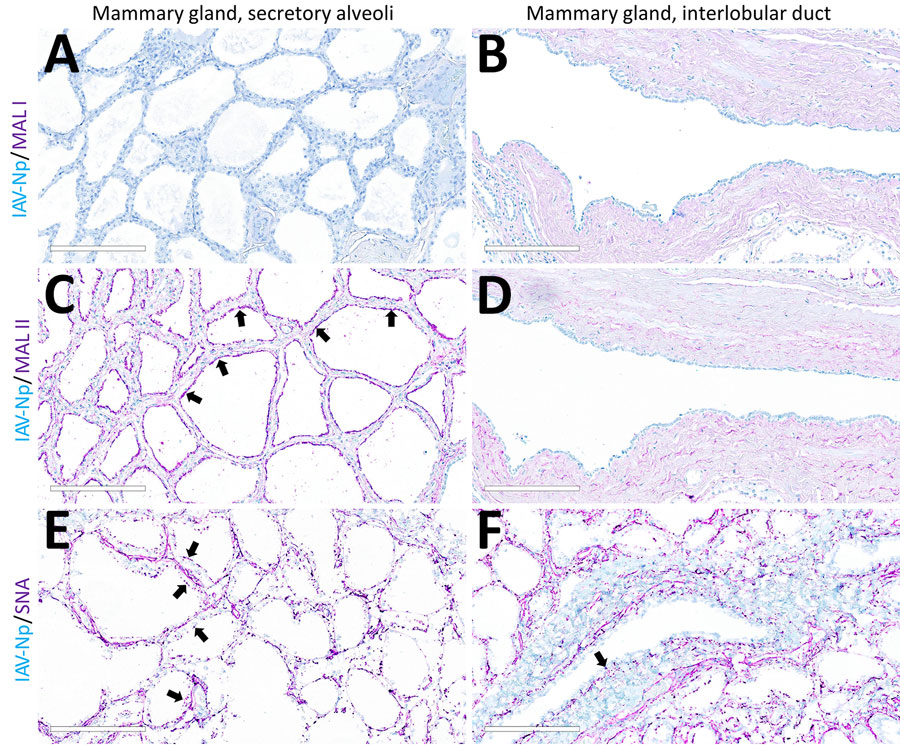
Figure 4. Unaffected region of the mammary gland from a US dairy cow infected with highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus, showing IAV-Np (teal chromogen), individually duplexed with MAL-I (magenta chromogen), MAL-II (magenta chromogen), and SNA (magenta chromogen) using chromogenic staining. Representative images of IAV-Np/MAL-I (A, B), IAV-Np/MAL-II (C, D), and IAV-Np/SNA (E, F) showing no IAV-Np labeling within unaffected mammary gland tissue sections. No MAL-I was detected in the mammary glandular (A) or interlobular duct epithelium (B). Within the alveolar gland epithelium, intense, granular, fibrillar labeling (arrows) of the apical portion labeling of MAL-II (C) was noted, with no epithelial labeling within the interlobular duct (D). Multifocal, strong, punctate, apical labeling (arrows) with SNA was observed within the mammary glandular epithelium (E). Scant apical labeling (arrow) was observed within the interlobular ductal epithelium with SNA (F). Scale bars indicate 200 μm. IAV-Np, influenza A virus nucleoprotein; MAL, Maackia amurensis lectin; SNA, Sambucus nigra lectin.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.