Volume 31, Number 12—December 2025
Research
Silent Propagation of Classical Scrapie Prions in Homozygous K222 Transgenic Mice
Figure 5
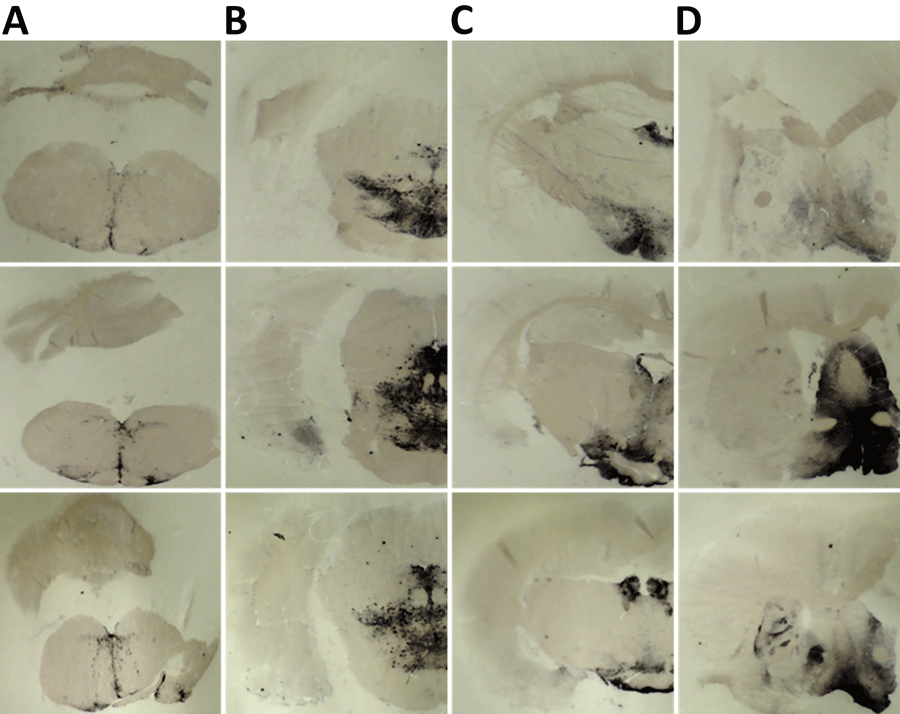
Figure 5. Paraffin-embedded tissue blotting results of brain tissues in study of propagation of classical scrapie prions. Images are of brain specimens from 3 distinct K222-Tg516 mice inoculated with CP060146/K222 goat isolate. Results are visualized with the Sha31 monoclonal antibody. A) Cerebellum specimens. B) Thalamus specimens. C) Hippocampus specimens. D) Cerebral cortex specimens. Proteinase K–resistant prion protein is visible as dark staining in similar brain regions in the 3 mice. Original magnification ×20.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: November 17, 2025
Page updated: January 01, 2026
Page reviewed: January 01, 2026
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.