Volume 11, Number 3—March 2005
Research
Rapid Identification of Emerging Pathogens: Coronavirus
Figure 2
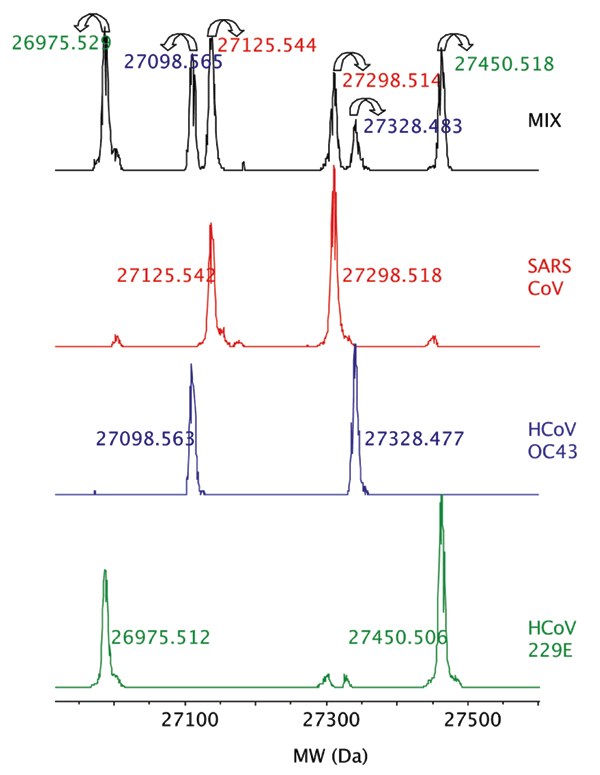
Figure 2. . Detection of 3 human coronavirus (CoV) in a mixture. The deconvoluted (neutral mass) mass spectra obtained for the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase primer for the 3 human CoV, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, and severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated CoV, which were tested individually and in a mixture are shown. Forward and reverse amplicons are shown with the measured monoisotopic masses for each strand. Colors of the monoisotopic masses for the mixed spectra correspond to the individual viral species.
Page created: April 25, 2012
Page updated: April 25, 2012
Page reviewed: April 25, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.