Volume 23, Number 12—December 2017
Research
Outbreaks of Neuroinvasive Astrovirus Associated with Encephalomyelitis, Weakness, and Paralysis among Weaned Pigs, Hungary
Figure 5
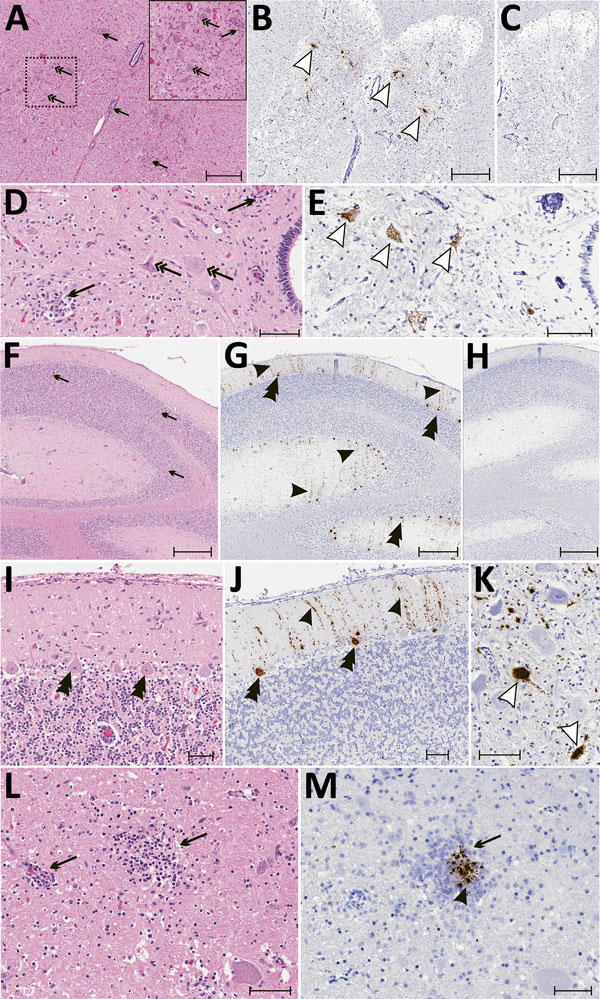
Figure 5. Results of histopathologic testing of central nervous system tissues from 2 symptomatic newly weaned pigs from a farm in Hungary. Sections of the cervical spinal cord (A–E), cerebellum (F–J), and cortex (L, M) from the index animal (GD-1) and the brain stem (K) from an additional affected stage 1 animal (GD-11). A, D, F, I, L) Hematoxylin and eosin stain. Gliosis (black arrows) is multifocal within the gray matter (panels A, D) and in the molecular layers (panels F, I, L and M). Neuronal degeneration and necrosis are evident by hypereosinophilia, angular degeneration, loss of neuronal detail, and vacuolation (double arrows in panels A, D). Some Purkinje neurons are slightly angular with mild vacuolation (double arrowheads in panel I). B, E, G, J, K, M) In situ hybridization of neuroinvasive porcine astrovirus. Hybridization of the neuroinvasive porcine astrovirus probe is restricted to neurons (white arrowheads in panels B, E, K) or limited to Purkinje neurons (double black arrowheads in panels G, J) with extension into dendritic processes that course through the molecular layer (black arrowheads in panels G, J). Hybridization of the neuroinvasive porcine astrovirus type 3 probe (black arrowhead in panel M) is present in the gliosis (black arrows in panels L, M). C, H) Using a control probe on a serial section, no hybridization is detectable. In situ hybridization. Scale bars indicate 500 µm (panels A–C, F–H) or 50 µm (panels D, E, I–M).